Cloud computing and IAM
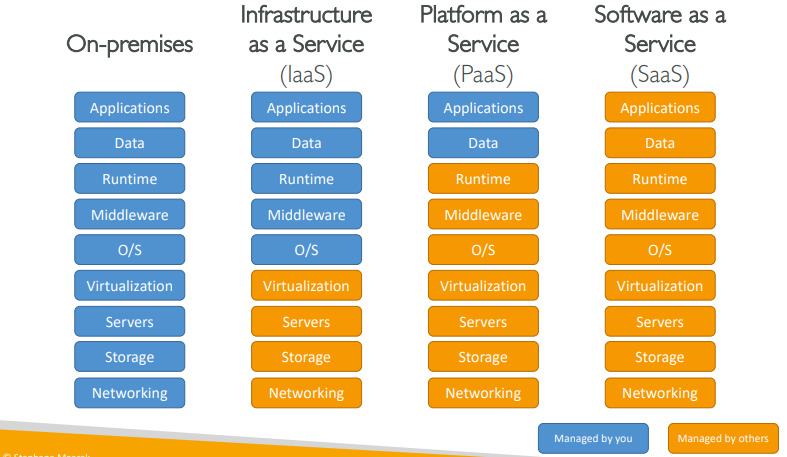
Types of Cloud Computing
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Provide building blocks for cloud IT
- Provide networking, computers, data storage space
- Highest level of flexibility
- Simulate the look from managing physical resources
- Eg: EC2, EBS, GCP, Digital Ocean, Elastic Load Balancing
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Remove the company to manage underlying infrastructure
- Focus on deployment and management of applications
- You will define the behavior and environment for your application (code)
- Eg: Heroku, ECS, Elastic Beanstalk
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Completed product that is run and managed by the service provider
- offer services meant to be accessed by end users
- Eg: Gmail, Outlook, Recognition for ML, Zoom
IAM
Users & Groups
- Root account shouldn´t be used or shared
- Users can be grouped, but not with groups, only users
- Users don´t have to belong a group, bout users can belong to multiple groups
- Users or groups can be assigned in JSON documents called policies
- In AWS you use the principle of least privilege
Policies
Consist of:
- Version: always include “2012-10-17”
- Id: an identifier of the policy(optional)
- Statements: one or more individual statements
- We can set password policy: uppercase letter, numbers, etc
- We can set a password expiration
AWS CLI Commands
- aws configure
- aws iam list-users
- you can use aws cloud shell in few regions (1gb free)
Shared Responsability Model for IAM
- AWS
- Infrastructure(global network security)
- Configuration and vulnerability analysis
- Compliance validation
- User
- Users, groups, roles, policies management and monitoring
- Enable MFA on all accounts
- Rotate all your keys often
- Use IAM tools to apply appropriate permissions
- Analyze access patterns & review permissions
Summary
- Users: mapped to a physical user, has a password for aws console
- Groups: contains users only
- Policies: JSON document that outlines permissions for users or groups
- Roles: For EC2 instances or AWS services
- Security: MFA + Pass Policy
- AWS CLI: manage AWS using command line
- AWS SDK: manage AWS services using programming language
- Access Keys: access AWS using CLI or SDK
- IAM Security Tools: IAM Credential Reports(account-level) & IAM Access Advisor(user-level)
EC2 Elastic Cloud Computing
IaaS highly configurable service
Instance Families
Are different combinations of CPU, Memory, Storage and Network capacity, allows you to choose the appropriate combination of capacity to meet your requirements
- General Purpose
- Balance of compute, memory and networking resources
- Use-cases: web servers and code repositories
- Compute Optimized
- Ideal for high performance processor
- Use-cases: scientific modeling, dedicated gaming servers and server engines
- Memory Optimized
- Fast performance for workloads that process large data sets in memory
- Use-cases: in-memory caches, in-memory databases, real time data analysis(bi)
- Accelerated Computing
- Hardware accelerators or co-processors
- Use-cases: Number calculations, graphics processing, data pattern matching
- Storage Optimized
- Designed for workloads that require sequential read and write access to very large datasets on local storage
- Use-cases: deliver tens of thousands of low-latency, random I/O operations per second (IOPS) to applications
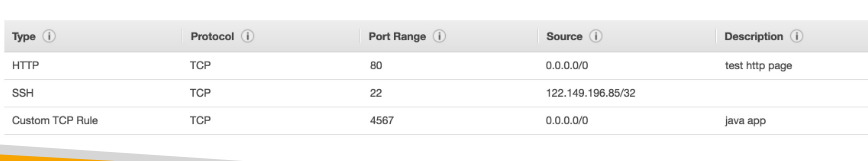
Security Groups
- Security Groups are the fundamental of network security in AWS
- They control how traffic is allowed into or out of our EC2 instances.
- Security groups only contain allow rules
- Security area acting as firewalls on EC2 instances
- They regulate:
- Access to ports
- Authorized IP ranges - IPv4 and IPv6
- Control of in/out bond network (from the instance to other or vice versa)
- Can be attached a multiple instances (M:M relation)
- Locked down to a region/VPC combination(if you switch to another region you have to create a new security group)
- Living outside the EC2, you wont see if traffic is blocked
- It’s good to maintain one separate security group for ssh access
- If your application is not accessible(time out) is because security group issue
- If your application gives a “connection refused” error, it’s an application error or is not launched
- By default all inbound traffic is blocked and all outbound traffic is authorized
EC2 Pricing Models
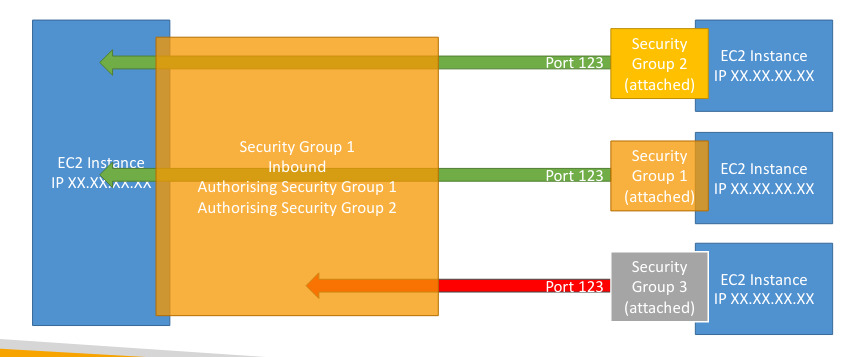
On-Demand (no upfront payment)
- good for low cost and flexible
- pay per second(windows and linux) pay per hour (other os)
- good for apps with short-term that can’t be interrupted
- good for apps that are tested for the first time
Reserved (up to 75%)
- predictable usage
- commit to ec2 over 1 or 3 year term
- can resell your unused instances
- if you want to change your hardware use convertible (up to 55%)
Dedicated (expensive)
- dedicated servers
- can be on-demand or reserved spot
- when you need isolate hardware (enterprise requirements)
Spot (up to 90%)
- request the unused ec2 capacity
- apps that have flexible starts and ends
- Users who need large amount of extra capacity
- unexpected shutdowns
Summary
- EC2 Instance: AMI(OS) + Instance Size(CPU+RAM) + Storage + Security Groups + EC2 User Data
- Security Groups: Firewall attached to the EC2 instance
- EC2 User Data: Script launched at the first start of an instance
- SSH: start a terminal in our EC2 via port 22
- EC2 Instance Roles: link to IAM roles
- Purchasing Options: On-Demand, Spot, Reserved, Dedicated host(expensive)/instances
EC2 Instance Storage
EBS Volume
- An EBS (Elastic Block Storage) Volume is a network drive you cant attach to your instances while they run
- EBS volumes will survive shutdowns and system crashes. That can be factor when work with sensitive data
- EBS volumes can be move around, mounted to other instances and converted to AMIs
- They can be mounted at one instance at a time and are bound to a specific availability zone
- Free tier: 30gb of free EBS storage (SSD or HDD)
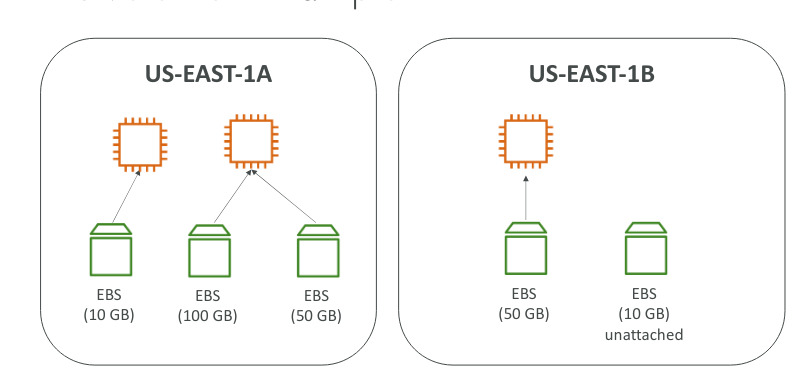
- By default the root EBS volume is deleted when finish the instance
- By default, any other attached EBS volume is not deleted (attribute disabled)
- This can be controlled by the AWS console or AWS CLI
- Use Case: preserve root volume when instance is terminated
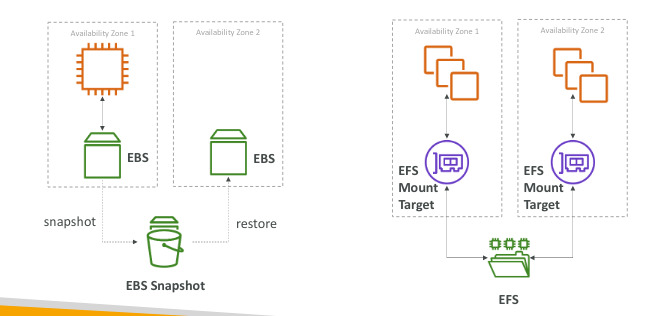
EBS Snapshots
- Make a backup of your EBS volume at a pint in time
- Not necessary to detach volume to do snapshot, but recommended
- Can copy snapshots across AZ or Regions
AMI
- Amazon Machine Image
- AMI are a customization of an EC2 instance
- You add your own software, configuration, os, monitoring,,,
- Faster boot, config time because all your software is pre-packaged
- AMI are built fr a specific region (and can be copied around regions)
- You can launch EC2 instances from AWS, your own or AWS marketplace AMI
AMI Process
- Start an EC2 instance and customize it
- Stop the instance (for data integrity)
- Build an AMI- this will create EBS Snapshots
- Launch instances from other AMIs
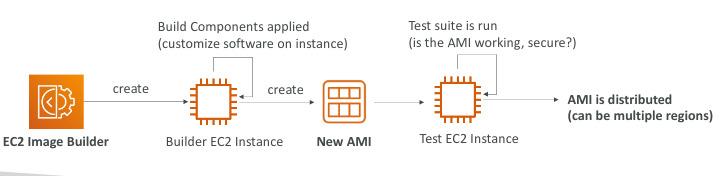
EC2 Image Builder
- Used to automate the creation of VMs or container images
- Automate the creation, maintain, validate and test EC2 AMIs
- Can be run on a schedule
- Free service (only pay for the underlying resources)
EC2 Instance Store
- EBS volume are network drives with good bout “limited” performance
- If you need a high performance hardware disk, use EC2 instance store
- Better I/O performance
- EC2 Instance Store lose their storage if they are stopped (ephemeral)
- Good for buffer/ cache /scratch data /temporary content
- Risk of data loss if hardware fails, and backups are your responsibility
EFS - Elastic File System
- Managed NFS (network file system) can be mounted in many EC2s
- EFS works with linux EC2 instances in multi-AZ
- Scalable, expensive (2xgp2), pay per use, no capacity planning
EBS vs EFS
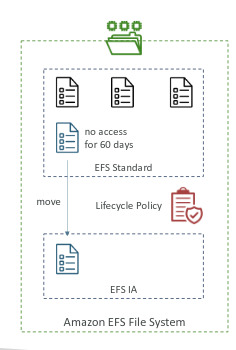
EFS Infrequent Access (EFS-IA)
- Storage class that is cost optimized for files that not accessed every day
- Up to 92% lower price than EFS standard
- EFS will move your files to EFS-IA based on the time of access
- Enable EFS-IA with a Lifecycle Policy
- Ex: Move files that are not accessed for 60 days
- Transparent to the app accessing EFS
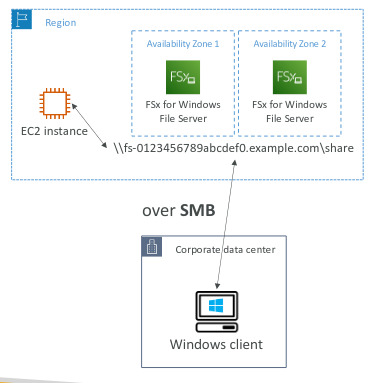
Amazon FSx for Windows File Server
- Fully managed, highly reliable and scalable windows native shared file system
- Built on Windows File Server
- Support SMB protocol & Windows NTFS
- Integrated with AD
- Can be accessed from AWS instances or on premise server
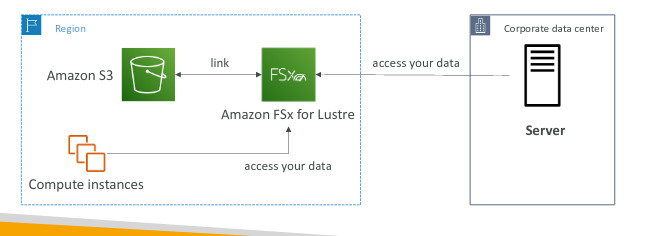
Amazon FSx for Lustre
- Fully managed, high performance scalable file storage for High Performance Computing (HPC)
- The name is derived for “linux” and “cluster”
- Use cases: ML, Analytics videos processing, Financial, Modeling
- Scales up to 100s GB/s, millions of IOPS, sub-ms latencies
Summary
- EBS Volumes
- network drives attached to one EC2, mapped in availability zones
- Can use EBS snapshots for backups/transfer to other AZ
- AMI: create ready to use EC2 instances with our customizations
- EC2 Image Builder: Automatically build, test and distribute AMIs
- EC2 Instance Store: High performance hardware disk attached to an ec2, lost if instance is stopped
- EFS-IA: cost-optimized storage class for infrequent accessed files
- FSx Linux/Windows: Network file systems for windows and high performance computing file system for Linux
ELB & ASG (Elastic Load Balancing & Auto Scaling Groups)
Scalability: ability to accommodate a larger load by making the hardware stronger(vertical), or by adding nodes (horizontal)
Elasticity: once a system is scalable, elasticity mean that there will be ‘auto scaling’, based on the load, this is cloud friendly : pay per use, match, optimize costs
Agility: (not related to scalability), new IT resources are only a click away, it mean that you reduce the time to make those resources available to your developers from weeks to minutes
Availability: goes in hand with horizontal scaling, mean running your application at least in 2 availability zones, the goal is to survive a data center loss (disaster)
Elastic Load Balancing
Load balancers are servers that forward internet traffic to multiple servers (EC2 instances) downstream
Use cases:
- Spread load across multiple downstream instances
- Expose a single pint of access (DNS) to your application
- Seamlessly handle failures of downstream instances
- Do regular health checks to your instances
- Provide SSL termination (HTTPS) for your websites
- High availability across zones
- Is managed by aws
- It cost less to setup your own load balancer, but it will be a lot more effort on your end (maintenance, integrations)
3 kinds of load balancers by AWS:
- Application load balancer (HTTP/HTTPS) -layer 7
- Network load balancer (ultra-high performance, allows for TCP) - layer4
- Classic load balancer (slowly retiring) - layer4 &7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
#!/bin/bash
#code for each instance
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl enable httpd
echo "<h1>hello world from $(hostname -f)</h1>" > /var/www/html/index.html
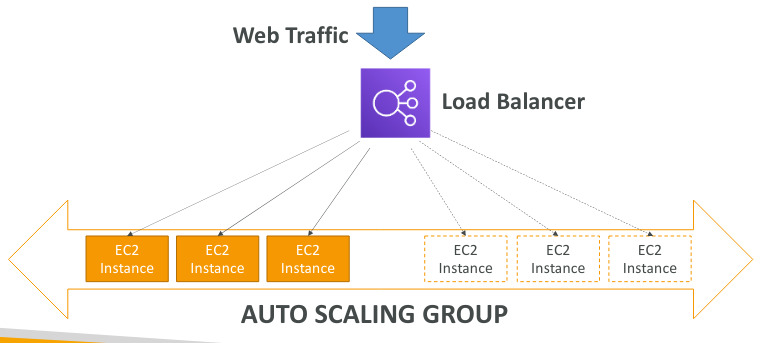
Auto Scaling Group
- In real life, the load on your websites and applications can change
- In the cloud, you can create and get rid of servers very quickly
- The goal of an Auto Scaling Group(ASG) is to:
- Scale out(add ec2 instances) to match an increased load
- Scale in ( remove ec2 instances) to match a decreased load
- Ensure we have a maximun and minimun of machines running
- Replace unhealthy instances
- Cost saving: only run at an optimal capacity (principle of the cloud)
Scaling strategies
- Manual scaling: Update the size of an ASG manually
- Dynamic Scaling: Respond to changing demand
- Simple/step scaling
- When a cloudwatch alarm is triggered (example CPU>70%) then add 2 units
- When a washcloth alarm is triggered (example CPU<30%) then remove 1
- Target tracking scaling
- Example: I want the average ASG CPU to stay around 40
- Sheduled Scaling
- Anticipate a scaling based on known usage patterns
- Ex: Increase the min capacity to 10 at 5pm on fridays
- Simple/step scaling
- Predictive Scaling
- Uses machine learning to predict future traffic ahead of time
- Useful when your load has predictable time based patterns
Summary
- Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)
- Distribute traffic across backend EC2 instances can be Multi-AZ
- Support health checks
- 3 types: Application (HTTP-L7), Network(TCP-L4), Classic(old)
- Auto Scaling Groups (ASG)
- Implement Elasticity for your application across multiple AZ
- Scale ec2 instances based on the demand of your system, replace unhealthy
- Integrated with ELB
Amazon S3
Amazon S3 Overview
- Allows people to store objects(files) in buckets(directories)
- Bucket must have a globally unique name (across all regions all accounts)
- Buckets are defines at the region level
- S3 look like a global service but buckets are created in a region
- Naming convention
- No uppercase
- No underscore
- 3-63 characters long
- Not an IP
- Must start with lowercase or number
- Objects have a key, the key is the FULL path
- s3://mybucket/myfile.txt
- The key is composed of prefix + object name
- s3://mybucket/myfolder/anotherfolder/myfile.txt
- There is no concept of “directories” within buckets, just keys with very long names that contain slashes(”/”)
- Object values are the content of the body
- Max object size is 5TB
- If uploading more than 5GB, must use “multi-part upload”
- Not charging for upload data, but you can download 1gb per month, then $0.09 per month
- Metadata (list of key/value pair)
- Tags(Unicode key/value pair)
- VersionID (if versioning is enabled)
S3 Security
- User based: IAM Policies - which API calls should be allowed for specific users from IAM
- Resource Based; Bucket Policies - bucket wide rules from s3 console- allows cross accounts
- Note: IAM Principal can access an S3 object if: the user IAM permission allows it OR the resource policy ALLOWS it AND there’s no explicit deny
- Encryption: you can encrypt objects using encryption keys
S3 Bucket Policies
- JSON based policies: resources:buckets and objects, actions: set of API allow or deny, Effect:allow/deny, Principal:the account to apply the policy on
- Use cases: grant public access to the bucket, force objects to be encrypted at upload, grant access to another account(cross account)
S3 Versioning
- Its enabled at bucket level
- Same key overwrite will increment the version
- Its best practice to version your buckets
- Protect against unintended deletes (easy roll back)
- Notes: any file not versioned when versioning have a version “null”, suspending versioning does not delete the previous versions
S3 Access Logs
- For audit purpose, you may want to log all access to S3 buckets
- Any request made to S3 will be logged into another S3 bucket
- That data can be analyzed and view suspicious patterns, etc…
S3 Replication (CRR & SRR)
- Must enable versioning in source and destination bucket
- Cross Region Replication (CRR)
- Compliance, lower latency access, replication across accounts
- Same Region Replication (SRR)
- Log aggregation, live replication between production and test accounts
- Buckets can be from different accounts, copying is asynchronous
- Must give proper IAM permission to S3
S3 Storage Class
S3 Durability and Availability
- Durability: High availability (99.999999..%, 11 9’s) of objects across multiple AZ
- Same for all storage classes
- Availability: Measures how readily available a service is
- S3 Standard has 99.99% availability, which means it will not be available 53 minutes a year
S3 Standard - General Purposes
- 99.99%, used for frequently accessed data
- Low latency and high throughput
- Sustain 2 concurrent facility failures
- Use cases: Big data analytics, mobile, gaming apps, content distribution
S3 Standard - Infrequent Access (IA)
- Suitable for data that is less frequently accessed, but requires rapid access when needed
- 99.9%, lower cost to S3 standard, but retrieval fee, sustain 2 concurrent facility failures
- Use cases: As a data store for disaster recovery, backups
S3 One zone - Infrequent Access (IA)
- Objects are stored in one Availability Zone, 99.5% availability
- Lower cost compared to S3-IA, the destruction of an AZ could result in the loss of objects stored in that zone.
- Use cases: Storing secondary backup of on-premise data, or storing data you can recreate
S3 Amazon Glacier & Glacier Deep Archive
- Designed for long-term archiving of object that rarely need to be retrieve, objects are stored using s3 glacier service
- U can’t retrieve an object in real time, instead you must initiate a restore request for the object and wait until restore is done: Expedited (1-5 min), Standard (3-5 hours), Bulk (5-12 hours) depends on the retrieval options
- Amazon Glacier deep archive - cheapest: Standard (12 hours), Bulk (48 hours)
S3 Intelligent-Tiering
- 99.9%, same low latency and high throughput performance of S3 standard
- Cost-optimized by automatically moving objects between two access tiers based on changing access patterns, you’re charged monthly monitoring and automation fee:
- Frequent access
- Infrequent access: if object hasn’t been accessed for 30 consecutive days
- Resilient against events that impact an entire Availability Zone
S3 Glacier Vault Lock
- S3 Object Lock:Adopt a WORM(Write once read many) model, block an object version deletion for an amount of time
- Glacier Vault Lock: Adopt a WORM model, lock the policy for future edits, helpful for compliance and data retention
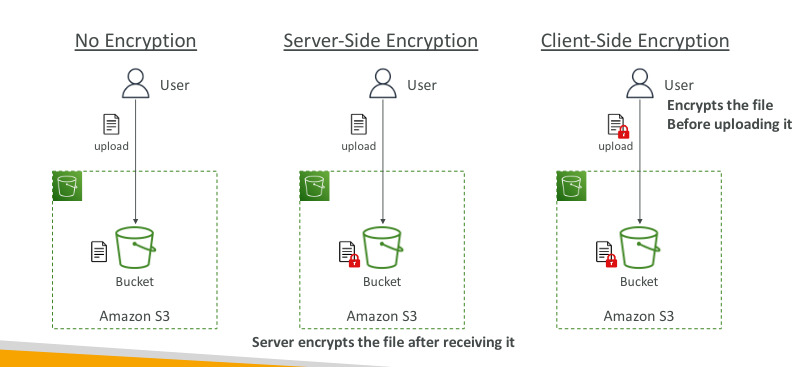
S3 Encryption
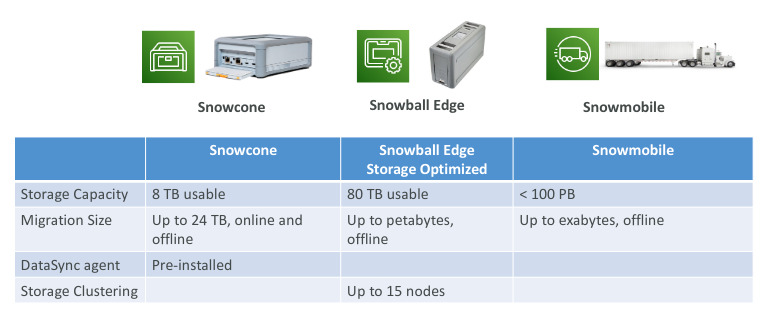
AWS Snow Family
- Highly secure, portable devices to collect and process data at the edge, and migrate data into and out AWS
- Data migration: snowcone, snowball edge, snowmobile
- Edge computing: snowcone, snowball edge
- Tip: If it takes more than a week to transfer over network, use snowball devices!
Snow Family - Usage Process
- Request Snowball devices from AWS console for delivery
- Install the snowball client/AWS OpsHub on your server
- Connect the snowball to your servers and copy files using the client
- Ship back the device when you’re done (goes to the right AWS facility)
- Data will be loaded into S3 bucket
- Snowball is completely wiped
What is Edge Computing?
- Process data while it’s being created on an Edge location
- A truck on the road, a ship on the sea, a mining station
- These locations may have no internet access, no computing power
- We setup a Snowball Edge/Snowcone device to edge computing to preprocess data, ML at the edge,etc
- Eventually we can ship back the device to AWS (to transferring data)
Snow Family - Edge Computing
- Snowcone (smaller): 2 CPU, 4gb ram, wired or wireless access
- Snowball edge (Compute optimized): 52 vCPUs, 208 ram, optional GPU, 42TB
- Snowball edge (Storage optimized): 40 vCPUs, 80 GB, object clustering
- All: Can run EC2 Instances & AWS Lambda functions (Using AWS IoT Green grass)
- Long term deployment options: 1 and 3 years discounted prices
AWS OpsHub
- Software GUI to manage your snow family device
- Unlocking clustered devices, transferring files, launching and managing instances, monitor device metrics, launch compatible AWS services on your devices
Hybrid Cloud for Storage
- AWS is pushing for “hybrid cloud”: part on premises and part on the cloud
- This can be due to: long cloud migrations, security requirements, compliance strategy, IT strategy
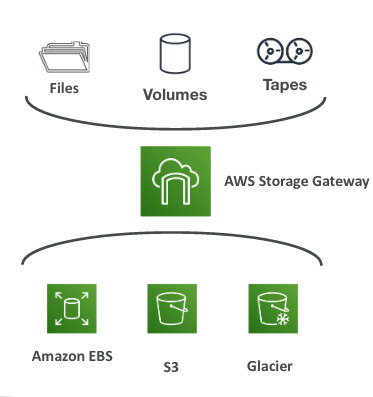
- S3 is a proprietary storage technology (unlike EFS/NFS), so how do you expose S3 data on premise? : AWS Storage Gateway
AWS Storage Gateway
- Hybrid storage service that allow to bridge what happens on premises directly into AWS cloud, using Amazon EBS, S3 and Glacier
- Use cases: disaster recovery, backup & restore
Amazon S3 - Summary
- Bucket vs Objects: global unique name, tied to a region
- S3 security: IAM policy, s3 bucket policy (public access), S3 encryption
- S3 Websites: host a static web on S3
- S3 Versioning: multiple versions for files, prevent accidental deletes
- S3 Access Logs: save logs from a bucket in another bucket
- S3 Replication: same region or cross region, must enable versioning and IAM permissions
- S3 Storage classes: Standard, IA, IZ-IA, Intelligent, Glacier, Glacier Deep Archive
- S3 Lifecycle Rules: transition objects between classes
- S3 Glacier Vault Lock/S3 Object Lock: WORM( Write Once Read Many)
- Snow Family: Import data onto S3 through a physical device, edge computing
- OpsHub: Desktop software to manage Snow Family devices
- Storage Gateway: hybrid solution to extend on-premises storage to S3
Databases & Analitycs
- AWS offers use to manage different databases
- Benefits:
- Quick Provisioning, High Availability, Vertical and Horizontal Scaling
- Automated Backup & Restore, Operation Upgrades
- Operating System Patching is handled by AWS
- Monitoring, alerting
- Many databases can run on EC2, but you must handle yourself the resiliency, backup, patching, high availability, fault tolerance, scaling
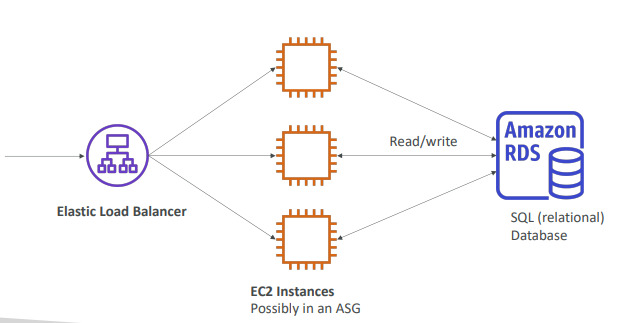
AWS RDS Overview
- Relational Database Service use SQL as a query languaje
- It allows you to create databases in the cloud that are managed by AWS:
- Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle, MSQL Server, Aurora(AWS)
Advantages using RDS over DB on EC2
- RDS is a managed service:
- Automated provisioning OS patching, continuous backups and restore points
- Monitoring dashboards, read replicas for improved read perform
- Multi AZ for Disasters and maintance windows for upgrades
- Scaling (horizontal and vertical), Storage backed by EBS
- CON: you can not SSH into your instances
Amazon Aurora
- Developed by AWS, not open sourced, not free tier
- PostgreSQL and MySQL are both supported by AuroraDB
- “AWS Cloud Optimized” and claims 5x performance improvement over MySQL on RDS, and over 3x performance on PostgreSQL on RDS
- Aurora storage automatically grows of 10GB up to 64TB
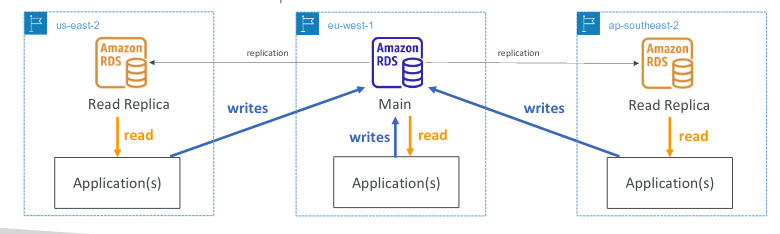
RDS Deployments: Read Replicas, Multi-AZ
- Read Replicas:
- Scale the read workload of your DB
- Can create up to 5 read replicas
- Data is only written to the main DB
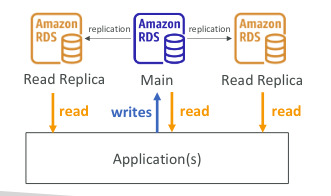
- Multi-AZ:
- Fail over: in case of AZ outage (high availability)
- Data is only read/written in the main database
- Can only have 1 other AZ as fail over
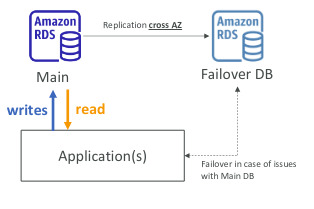
- Multi-Region(Read Replicas):
- Good for disaster recovery, local performance for global read and replication cost
![Untitled]()
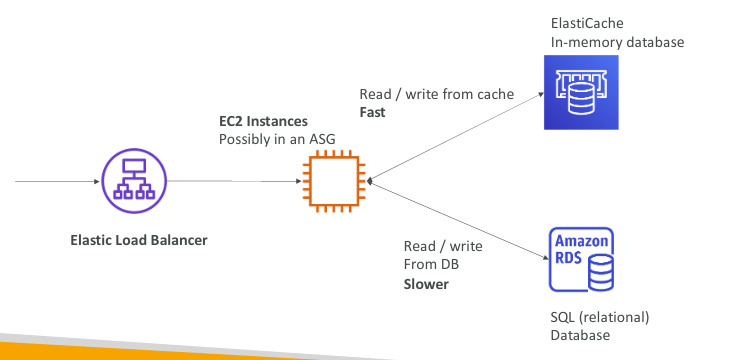
Amazon ElastiCache
- The same way RDS is to get managed Relational Database
- Elasticache is to get managed Redis or Memcached
- Caches are in-memory database with high performance, low latency
- Helps reduce load off databases for read intensive workloads
- AWS takes care of OS maintenance, patching, setup, configuration, monitoring recovery and backups
DynamoDB
- Fully managed key/value database highly available with replication across 3 AZ, minimum of 99,99 percent of availability in a single region
- NoSQL Database, fast and consistent in performance
- Scales to massive workloads, distributed serverless database
- Single-digit millisecond latency, integrated with IAM for security, authorization and administration
- Low cost and auto scaling capabilities, two pricing models (on demand/provisioned capacity mode)
DynamoDB Accelerator - DAX
- Fully Managed in-memory cache for DynamoDB
- 10x performance improvement - single- digit millisecond latency to microseconds latency - when accessing your DynamoDB tables
- Secure,highly scalable and available
- Note: DAX is only used with DynamoDB and ElastiCache for other databases
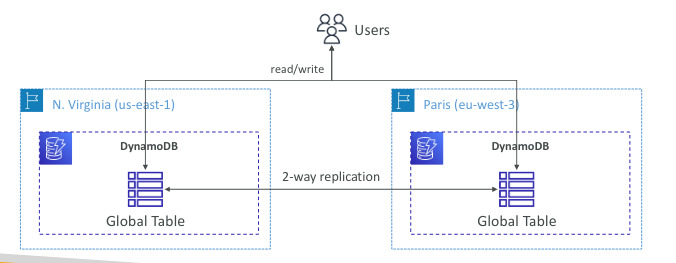
DynamoDB - Global Tables
- Make a Table accessible with low latency in multiple-regions
- Active-Active replication (Read/Write in any AWS Region)
Redshift
- Based in PostgreSQL, but it’s not used for OLTP
- It’s OLAP - online analytical processing (analytics and data warehousing)
- Load every hour, not every second
- 10x better performance than other data whouses, scale to PBs of data
- Columnar Storage of data (instead of row based)
- Massive Parallel Query (MPP), pay as you go on the instances provisioned
- Has a SQL interface for performing queries
- BI tools such as AWS Quicksight or Tableau integrate with it
- Redshift Spectrum can analyze structured data stored in S3
- Dense compute node uses magnetic disks (max 326TBs of data) and dense storage nodes use SSDs (max 2PBs of data)
Amazon EMR
- Elastic MapReduce
- Help creating Hadoop cluster (big data) to analyze and process vast data
- The clusters can be made of hundreds of EC2 instances
- Support Apache Spark, HBase, Presto, FLink
- EMR takes care of all the provisioning and configuration
- Auto-scaling and integrated with spot instances
- Use cases: data processing, machine learning, web indexing, big data.
Amazon Athena
- Serverless query service to analyze data stored in Amazon S3
- Uses standard SQL language to query the files
- Supports CSV, JSON, ORC, Avroa and Parquet
- $5.00 per TB of data stored, use compressed or columnar data for cost-savings (less scan)
- Use cases: BI, analytics, reporting, analyze & query VPC logs, cloud trail, etc
Amazon QuickSight
- Serverless machine learning-powered business intelligence service to create interactive dashboards
- Fast automatically scalable, embeddable, with per-session pricing
- Use cases: Business analytics, building visualizations, perform ad-hoc analysis, get business insights
- Integrated with RDS, Aurora, Athena, Redshift, S3, …
Document DB
- Aurora is an “AWS implementation” of PostgreSQL or MySQL
- DocumentDB is the same for MongoDB (No SQL database), also similar implementation of aurora
- MongoDB is used to store, query and index JSON data
- Fully managed, highly available with replication across 3AZ
- Aurora storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, to 64TB
- Automatically scales to workloads with millions of request per second
Amazon Neptune
- Fully managed graph database
- Popular graph datasets would be a social network
- Users have friend, post have comments, comment have likes
- Highly available across 3 AZ, with up to 15 read replicas
- Build and run application working with highly connected datasets - optimized for these complex and hard queries
- Can store billions of relations and query the graph with milliseconds of latency
- Great for knowledge graphs, fraud detection, recommendation engines, social network
Amazon QLDB
- Quantun Ledger Database is a book recording financial transactions
- Fully managed, serverless, high available, replication across 3 AZ
- Used to review history of all the changes made to your application data over time
- Inmutable system: no entry can be removed or modified, cryptographically verifiable
- 2-3x better performance than common ledger blockchain framework, manipulate data using SQL
- QLDB has a central database, in line with many financial regulations rules, in Amazon Managed Blockchain exists decentralization
Amazon Managed Blockchain
- Blockchain makes possible to build applications where multiple parties can execute transactions without the need for a trusted, central authority
- Use cases: join public blockchain networks or create your private network, compatible with the frameworks Hyperledger Fabrid & Ethereum
DMS - Database Migration Service
- Quickly and securely migrate databases to AWS, resilient, self healing
- The source database remain available during the migration
- Supports: Homogeneous migrations or Heterogeneous migrations ( ex: SQL server to Aurora)
Summary
- Relational Database - OLTP: RDS and Aurora (SQL)
- In- memory database: Elasticache
- Key/value database: DynamoDB(serverless) & DAX(cache for DynamoDB)
- Warehouse - OLAP: Redshift (SQL)
- Hadoop cluster: EMR
- Athena: query data on Amazon S3 (serverless & SQL)
- Quicksight: dashboards on your data (serverless)
- Document DB: “Aurora for Mongo DB” (JSON-NoSQL database)
- Amazon QLDB: Financial Transactions Ledger (inmutable)
- Amazon Managed Blockchain: managed Hyperledger Fabric & Ethereum
- Databases Migration: DMS, and netpune for graph database
ECS, Lamda, Batch, Lightsail
ECS
- Elastic Container Service, launch docker containers on AWS
- You must provision & maintain the infrastructure (EC2 instances)
- AWS takes care of starting and stopping of containers, works with Application Load Balancer
Fargate
- Launch Docker containers in AWS
- **You do not provision the infrastructure ( no EC2 to manage), simpler!
- Serverless offering, AWS just run container fir you based on CPU-RAM you nedd
ECR
- Elastic Container Registry
- Private Docker Registry on AWS, this is where you store your docker images so they can run by ECS or Fargate
What is serverless?
- New paradigm in which developers don´t manage the server anymore, just deploy code (amazon S3, Dynamo DB, Fargate, Lambda)
- Serverless was pioneered by AWS Lambda but now also includes databases, messaging, storage, etc
- Serverless does not mean there are no server, it means you just don’t manage them
AWS Lambda
- Compared to EC2, has virtual functions, this mean no servers to manage
- Limited by time, short executions, run on-demand and the scaling is automated
- Easy pricing: pay per request and compute time, free tier of 1 million of Lambda Request and 400GB of compute time
- Integrated with the whole AWS suite of services
- Easy monitoring through AWS Cloud Watch, easy to get more resources per functions (up to 10GB of ram)
- Increasing RAM will also improve CPU and network
- Languages support: Node.js, python, java, C#, golang, Ruby, Lambda Container image, the container image must implement the lambda runtime API
AWS Lambda Pricing
- Pay per calls first million request are free, then 0.20 per million request
- Pay per duration: 400gbs seconds of compute per month are free
- 400,000 seconds if function is 1GB ram
- 3200000 seconds if function is 128 MB ram
- After that $1,00 for 600,000 Gb seconds
- Usually is very cheap to run AWS Lambda so its very popular
Amazon API Gateway
- Ex: Building a serverless API
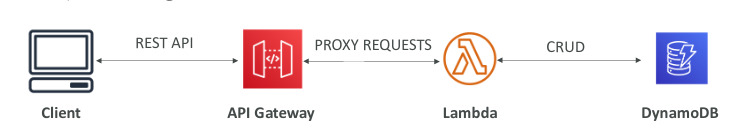
- Fully managed service for developers to easily create, publish, maintain, monitor and secure APIs
- Serverless and scalable, supports RESTful APIs and WebSocket APIs, security, user auth, API throttling, API keys
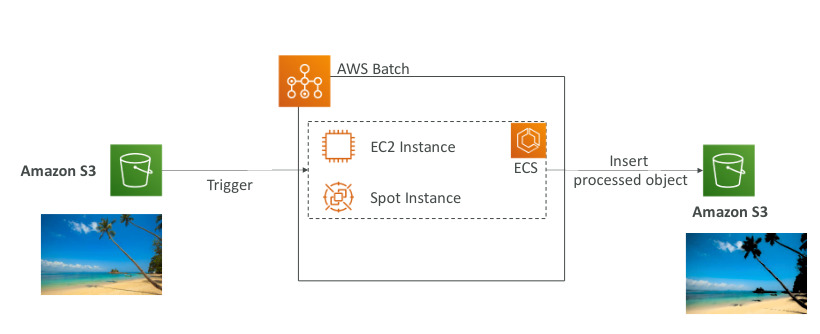
AWS Batch
- Fully managed batch processing at any scale
- A batch job is a job with a start an end, so batch jobs will dynamically launch EC2 Instances or Spot instances
- AWS Batch provisions the right amount of compute/memory
- Batch jobs are defined as Docker Images and run on ECS
Batch vs Lambda
- Lambda
- Time limit, so limited runtime
- Limited temporary disk space, serverless
- Batch
- No limited time, run as long as it’s packaged as a Docker image
- Rely on EBS/instance store for disk space
- Relies on EC2 (can be managed by AWS)
Amazon Lightsail
- Virtual servers, storage, databases and networking
- Low and predictable pricing, simpler alternative to using EC2, RDS, ELB, Route 53
- Great for people with little cloud exp, like me!
- Use cases: simple web apps(Lamps, Nginx, Mean, Node.js), Websites(Wordpress, Magento, Joomla),dev or test environments
- Has high availability but no auto-scaling, limited AWS integrations
Summary
- Docker: container technology to run applications
- ECS: run docker containers on EC2 instances
- Fargate: run docker without provisioning infrastructure, serverless
- ECR: private docker images repository
- Batch: run batch jobs on AWS across managed EC2 Instances
- Lightsail: predictable & low pricing for simple application & DB stacks
- Lambda:
- Serverless, function as a service, seamless scaling, reactive
- billing:by the time run x by the RAM provisioned, by the number of invocations
- Languages support: many languages except docker(only with api)
- Invocation time: up to 15 minutes
- Use cases: create thumbnails for images uploaded in S3, run a serverless cron job
- API Gateway: expose Lambda functions as HTTP API
Deployments & Managing Infrastructure at Scale
CloudFormation
- Is a declarative way of outlining your AWS Infrastructure, for any resources
- Ex: within a CloudFormation template, you say: i want a security group, running two EC2 instances with a load balancer in front of these machines
- Then CloudFormation crates those for you, in the right order, with the exact configuration that you specify
- Infrastructure as code
- No resources are manually created, which is excellent for control
- Changes to the infrastructure are managed through code
- Cost
- You can estimate your cost using CloudFormation template
- Saving strategy: In Dev, you could automation deletion of templates at 5PM and recreated at 8AM, safely
- Productivity
- Ability to destroy and recreate an infrastructure on the cloud on the fly
- Automate the generation of Diagram for your templates, declarative programming(no need to figure out ordering and orchestration)
- Support almost all AWS resources, and use “custom resources” for resources that are not supported
- Stack designer
- We can see all the resources and the relation between the components
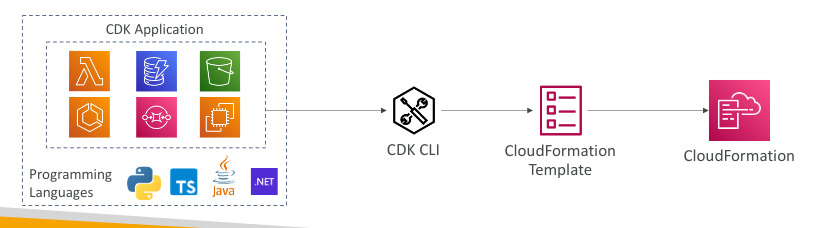
AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK)
- Define your cloud infrastructure using a familiar language:java script, typescript, python, java and .net
- The code is compiled into a CloudFormation template (JSON/YAML)
- You can therefore deploy infrastructure and application runtime code together
- great for lambda functions and docker containers
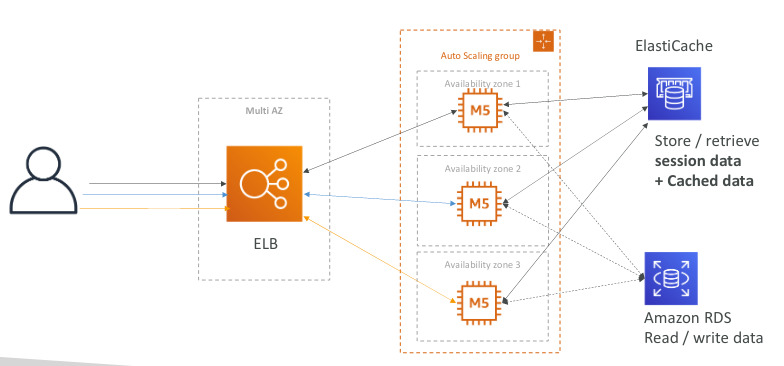
Typical architecture: Web app 3-tier
AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Is a developer centric view of deploying an application on AWS
- Use all components (EC2,ASG,ELB,RDS…) and we have full control over configuration
- Beanstalk= Platforms as a Service (PaaS)
- You paying for the underlying instances
- Managed service:
- Instance config and os is handled by beanstalk
- Load balancing and auto scaling, app monitoring and responsiveness
- Just the application code is responsibility of the developer
- Three architecture models:
- Single instance deployment: good for dev
- LB + ASG: great for production of web apps
- ASG only: great for non-web apps in production
- Health Monitoring
- Health agent pushes metric to CloudWatch
- Checks for app health, publishes health events
AWS CodeDeploy
- We want to deploy our application automatically
- Works with EC2, on premise server and Hybrid service
- Servers/Instances must be provisioned and configured ahead of time with de CodeDeploy Agent
AWS CodeCommit
- Before pushing the app code to servers, it need to be stored somewhere
- Instead of using Github, AWS provides CodeCommit
- Make it easy to collaborate with others on code, the code changes automatically versioned
- Fully managed, scalable & highly available, private, secured and integrated with AWS
AWS CodeBuild
- Compiles source code, run tests and produces packages that are ready to be deployed( by codedeploy for example)
- Fully managed, serverless, continuosly scalable & highly available, secure, only pay for the build time
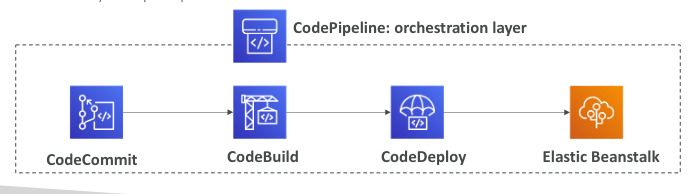
AWS CodePipeline
- Orchestrate the different steps to have the code automatically pushed to production
- Code → Build → Test → Provision → Deploy
- Basis for CICD (Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery)
- Fully managed, compatible with CodeCommit, CodeBuild,… Fast delivery and rapid updates
AWS CodeArtifact
- Software packages depend of each others, storing and retrieving these dependencies is called artifact management
- CodeArtifact is a secure, scalable, and cost-effective artifact management for software development
- Developers and CodeBuild can then retrieve dependencies straight from CodeArtifact
AWS CodeStar
- Unified UI to easily manage software development activities in one place
- Quick way yo get started to correctly setup CodeCommit, CodePipeline, Codebuild, Codedeploy, etc
- Can edit the code in the cloud using AWS Cloud9
AWS Cloud9
- Is a cloud IDE for writing, running and debugging code
- A cloud IDE can be used within a web browser, meaning you can work on your projects from your office and has collaboration in real time (pair programming)
AWS Systems Manager(SSM)
- Helps you manage your EC2 and On-Premises systems at scale
- Another hybrid AWS service, get operational insights about the state of your infra
- Patching automation for enhanced compliance and run commands across and entire fleet of servers
- Works with Windows and LInux
- How works:
- We need to install SSM on the system we control
- Installed by default in Amazon LInux AMI & Ubuntu AMI
- If an instance cant be controlled by SSM it’s probably an issue with the SSM agent.
- SSM Agents enable us to run commands, patch & configure our servers
Systems Manager - SSM Session Manager
- Allows you to start a secure shell on your EC2 and on-premise servers
- No SSH access, bastion hosts, or SSH keys needed, no port 22 need (best practice)
- Support Linux, MacOS, Windows, send session log data to S3 or CloudWatch logs to be more secure
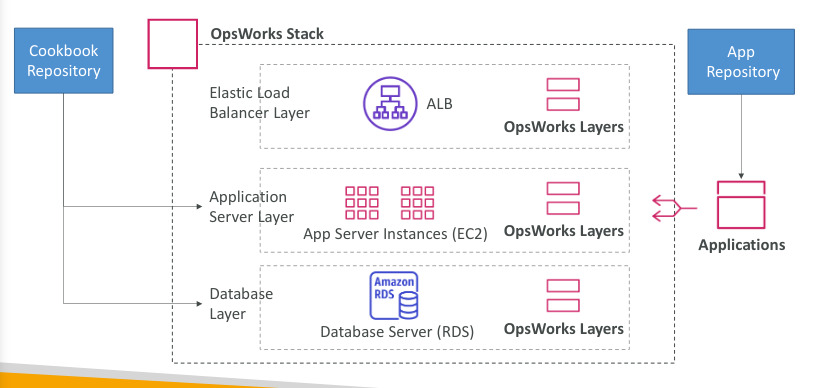
AWS OpsWorks
- Chef and Puppet help you perform server config automatically, or repetitive actions
- Work great with EC2 and On-Premises VM
- Alternative to AWS SSM, only provision standard AWS resources (EC2, Databases, Load Balancer, EBS)
- Chef or Puppet needed → AWS OpsWorks
Deployment - Summary
- Cloud Formation (AWS only): infra as code, works with all AWS resources, repeat across Regions and Accounts
- Beanstalk (AWS only): platforms as a service, limited to certain programming languages or docker, deploy code with a known architecture (ALB+EC2+RDS)
- Code Deploy (hybrid): deploy and upgrade any applications onto servers
- System Manager (hybrid): patch, configure and run commands at scale
- OpsWorks (hybrid): managed Chef and Puppet in AWS
- Code commit (store code in git repo), CodeBuild (build and test code in AWS), CodeDeploy (deploy code onto servers), CodePipelines (orchestration of pipeline), CodeArtifact: store software packages, dependencies, Code Star (unified view to quick start of using the other services), Cloud9 (cloud IDE with collab), AWS CDK (define your cloud infrastructure using a programming language)
Global Infrastructure
- On AWS: this could be Regions or Edge Locations
- Decreased latency: deploy your apps closer to your users to decrease latency
- Disaster Recovery (DR): you can fail-over another region to have your app still working, increase availability
- Attack Protection: distributed global infrastructure is harder to attack
- Regions: For deploying applications and infrastructure
- Availability Zones: Made of multiply data centers
- Edge Locations (Points of presence): for content delivery as close as possible to users
- Global DNS: Route 53: great to route users to the closest deployment, great for disaster recovery strats
- Global Content Delivery Network (CDN): CloudFront: Replicate part of your apps to AWS Edge locations- decrease latency and cache common requests-improved user experience
- S3 Transfer Acceleration: Accelerate global uploads and downloads into Amazon S3
- AWS Global Accelerator: Improve availability and performance using the AWS network
Amazon Route 53
- Managed DNS, collection of rules and record which helps clients understand how to reach server through URLs
- Routing Policies: simple (no heath checks), weighted (with weights for each server), latency (the lowest latency), failover (based on health check)
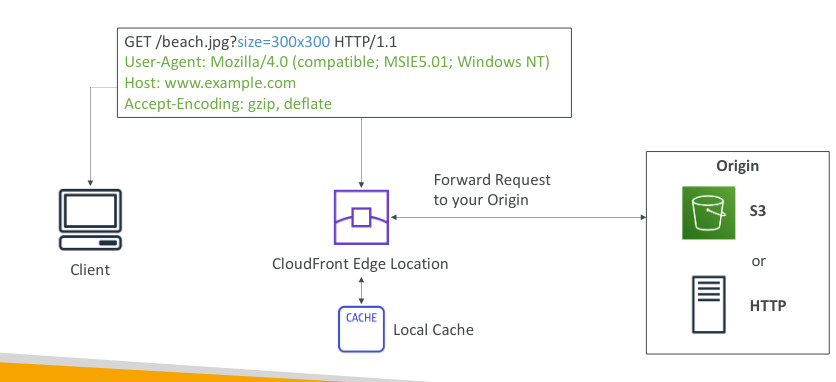
AWS CloudFront
- Content Dleivery Network (CDN)
- Improves read performace, content is cached at the edge
- 216 point of presecnce (edge locations)
- DDoS protection, integration with shiel, AWS WAF
- Origins:
- S3 bucket: distributing files and caching them at the edge, enhanced security with Origin Access Identity (OAI)
- Custom Origin (HTTP): application load balancer, ec2 instances, s3 website…
CloudFront vs S3 Cross Region Replication
- CloudFront:
- Global edge network, files are cached for a TTL
- Great for static content that must be available everywhere, ex:website)
- S3 Cross Region Replication:
- You choose the region you want replication to happen, files are updated in real time (read only)
- Great for dynamic content that needs to be available at low-latency in few regions
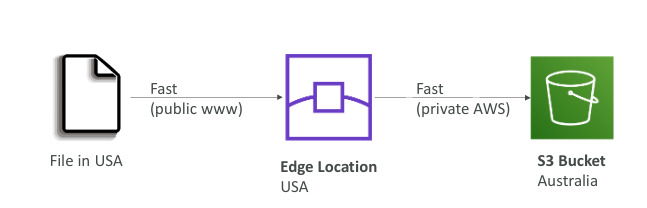
S3 Transfer Acceleration
- Increase transfer speed by transferring file to an AWS edge location which will forward the data of the S3 in the target region
AWS Global Accelerator
- Improve global application availability and performance using AWS global network
- 2 Anycast IP are created for you app and traffic is sent through Edge Locations
- The Edge Location sent the traffic to your app
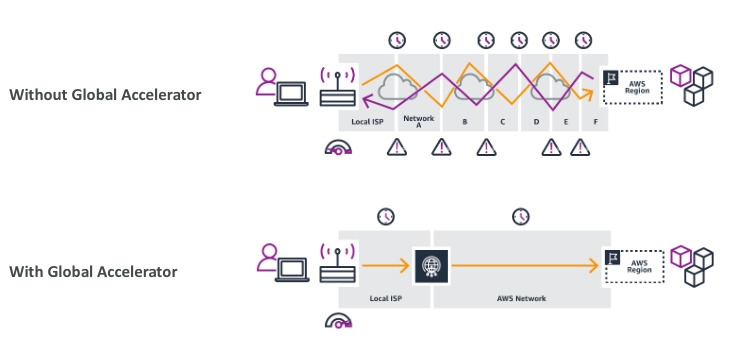
AWS Global Accelerator vs CloudFront
- They both use AWS global network and it’s edge locations around the world
- Both using DDoS protection
- Cloudfront (CDN): improves performance for cacheable content, content is server at the edge
- Global Accelerator: No caching proxying packets an the edge, good for HTTP that require static IP adress
AWS Ouptosts
- AWS Outposts are “server racks” that offer the same AWS infrastructure, services, APIs and tools to build your own apps on-premises just as in the cloud
- AWS will setup and manage “outposts racks” within your on-premise infra and you can start leveraging AWS services on-premises
- You are responsible for the Outposts Rack physical security
- Benefits:low latency access to on-premise, local data processing, data residency, easier migration to the cloud, fully managed services
AWS WaveLength
- Infrastructure deployments embedded within communications providers datacenter at the edge of the 5G networks
- Bring AWS services to the edge of the 5G networks, ultra low latency through 5G
- Use cases: smart cities, ML- assisted diagnostics, real time gaming
AWS Local Zones
- Places AWS compute, storage, database closer to end users to run latency-sensitive applications
- Extend your VPC to more regions, compatible with EC2,RDS,ECS,EBS,…
- Ex: AWS Regions: N. Virginia (us-east-1), Local Zones: Boston, Chicago, Dallas….
Global Application Architecture
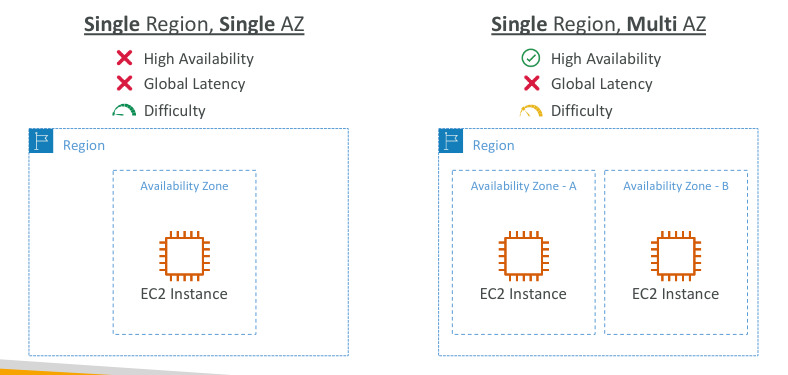
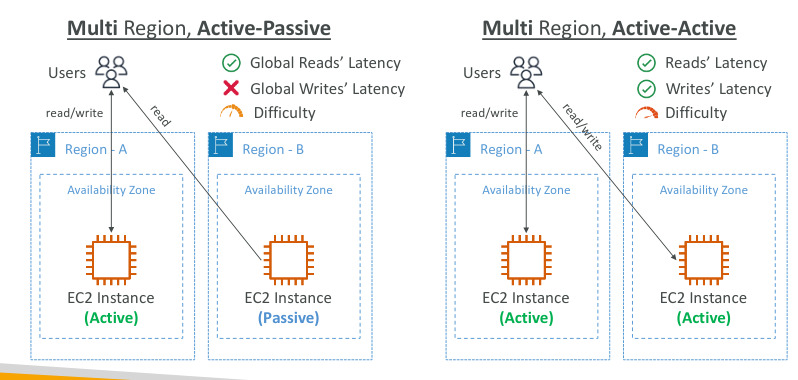
Global Applications in AWS - Summary
- Global DNS: Route 53: route users to the closest deployment, great for disaster recovery strategies
- Global Content Delivery Network (CDN): Cloudfront: Replicate part of your application to AWS Edge Locations, cache common requests. improve user experience and low latency
- S3 Transfer Acceleration: Accelerate global uploads and download in Amazon S3
- AWS Global Accelerator: Improve global application availability and performance over network
- AWS Outposts: Deploy outposts racks in your own data center to extend AWS services
- AWS WaveLenght: Bring AWS to the edge of the 5G networks, ultra low latency
- AWS Local Zones: Bring AWS resources (compute, storage, database) closer to your users, good for latency.sensitive applications
Cloud Integrations
- Synchronous communications: app to app ( ex: buying service and shipping service)
- Asynchronous: app to queue to app
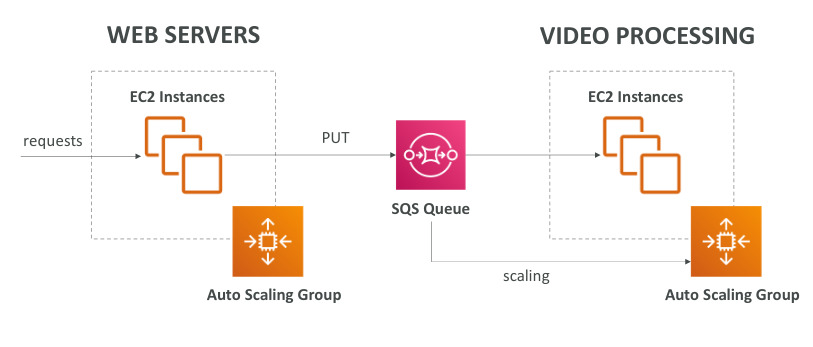
- If there are sudden spikes of traffic you have to decouple your app using SQS; queue model, SNS:pub/sub model, Kinesis: real-time data streaming model
Amazon SQS - Simple Queue Service
- Oldest AWS offering, serverless, use to decouple applications
- Scales from1 to 10,000 messages per second
- Default retention of 4 days, max of 14 days, no limit how many messages in queue
- Messages are deleted after the read, low latency(<10 ms on publish and receive)
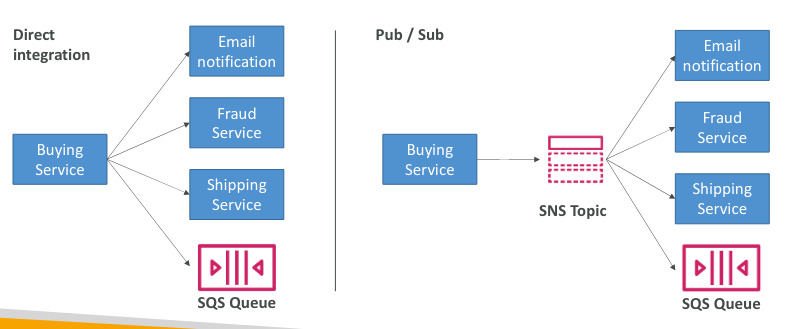
Amazon SNS
- Simple Notification Service, the “event publishers” only sends message to one SNS topic
- As many event subscribers as we want to listen to the SNS notifications
- Each subscriber will get all the messages
- Up to 10 million subscribers per topic, 100,000 topic limit
- SNS subscribers can be: http/https, emails, SMS, Mobile notifications, SQS queues, Lambda Functions
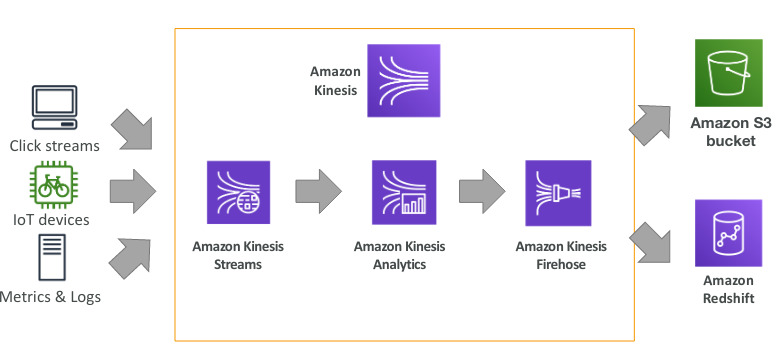
Amazon Kinesis
- Kinesis= Real time big data streaming
- Managed service to collect, process and analyze real-time streaming data at any scale
- Kinesis data firehose: load streams into S3, redshift, elasticsearch…
- Kinesis data streams: low latency streaming to ingest data at scale from hundreds of sources
- Kinesis data analytics: perform real time analytics on streams using SQL
- Kinesis video streams: monitor real time video streams for analytics or ML
Amazon MQ
- Only when need using open protocols on-premise servers : MQTT, AMQP, STOMP, WSS
- When migrating to the cloud, instead of re-engineering the applicaction to use SQS and SNS, we can use AmazonMQ= Managed Apache ActiveMQ
- Doesn’t scale as much as SQS/SNS, these are cloud native, and serverless, Amazon MQ run on dedicated machine
Integration Section - Summary
- SQS:queue service in AWS, multiple producers, messages are kept up to 14 days, used to decouple applications
- SNS: notifications service in AWS, email, lambda, SQS, HTTP, mobile, multiple subs, send all messages to them, no message retention
- Kinesis: real time data streaming, persistence and analysis
- Amazon MQ: managed Apache MQ in the cloud (MQTT, AMQP.. protocols)
Cloud Monitoring
Amazon CloudWatch Metrics
- CloudWatch provides metric for every services in AWS
- Metric have timestamps, can create dashboards
- Important Metrics:
- EC2 Instances: cpu utilization, status checks, every 5 minutes, you can pay for detailed monitoring (1min)
- EBS Volumes: disk read and writes
- S3 Buckets: total estimated charge(us-east-1)
- Service Limits: how much you use a service API
- Custom metrics: push your own metrics
Amazon CloudWatch Alarms
- Trigger notification for any metric
- Alarms actions: auto scaling: increase o decrease EC2 instances, EC2 actions: stop, terminates, reboot an EC2 instance, SNS Notifications: send a notification into an SNS topic
- Can choose the period on which to evaluate an alarm
- Ex: create a billing alarm on cloudwatch billing metric, ALARM STATES: OK, INSUFFICIENT_DATA, ALARM
Amazon CloudWatch Logs
- CloudWatch Logs can collect logs from:Elastic Beanstalk, ECS, Lambda, Cloud trail, Route53
- Enables real-time monitoring of logs
- Adjustable CloudWatch Logs retention
Cloud Watch Logs for EC2
- By default, no logs from EC2 instance will go to CloudWatch
- You need to run a CloudWatch agent on EC2 to push the log files you want
- The CloudWatch Log agent can be setup on-premises too and make sure IAM permissions are correct
Amazon EventBridge
- EventBridge is the next evolution of CloudWatch Events
- Default event bus. generated by AWS services (CloudWatch Events)
- Partner event bus. receive events from SaaS service or apps
- Custom Event Buses: for your own applications
- Schema Registry: model event schema
- EventBridge has a different name to mark the new capabilities
- The cloudWatch events name will be replaced with EventBridge
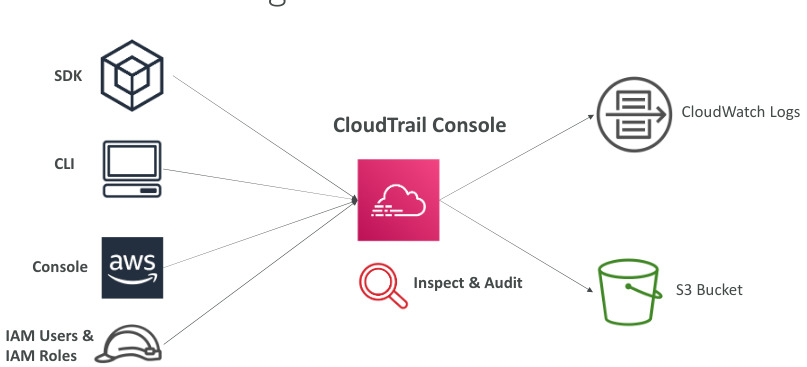
AWS Cloud Trail
- Enabled by default and provides governance, compliance and audit for your AWS Account
- Gets an history of events or API calls made in your AWS Account by: console, SDK, CLI, AWS Services
- You can put these logs into CloudWatch logs or S3, and a trail can be applied to all regions(default) or a single one, if a resource is deleted investigate cloud trail first
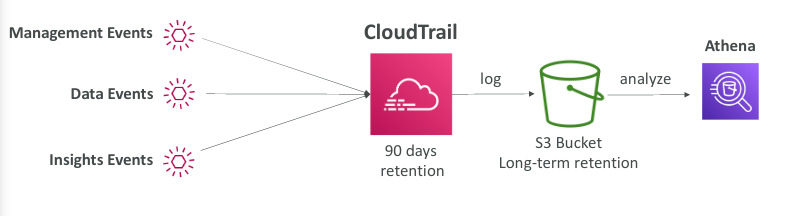
Cloud Trail Events
- Management events: operations that a principal (user or service) attempts to execute against an AWS resource. this include write-only events (create ec2) and read only events (list ec2 instances)
- Data events: consist of S3 object-level activity and lambda functions executions, both of which tend to be a high volume, CloudTrail draw a distinction to S3 events, read only(get-object) and write only(put object)
Cloud Trail Events Retention
- Events are stored for 90 days in CloudTrail
- To keep events beyond this period, log them to S3 and use athena
AWS X-Ray
- Debugging in Production, old way: test locally, add log everywhere, re-deploy in production
- Debugging: one big monolith “easy”, distributed services “hard”
- No common views of your entire architecture
- Use cases:
- Troubleshooting performance
- Understand dependencies in a microservice architecture
- Review request behavior, find error and exceptions
- Where i am throttled, identify users that are impacted
Amazon CodeGuru
- ML-powered service for automated code reviews and application performance recommendations
- Two functions:
- CodeGuru Reviewer: automate code reviews for static code analysis
- CodeGuru Profiler: visibility or recommendation about application performance during runtime
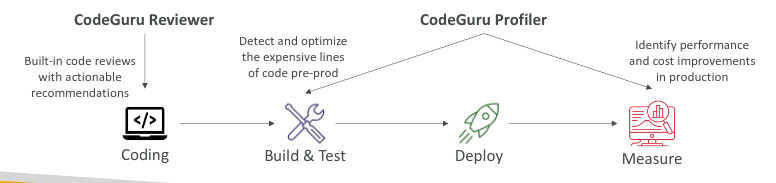
CodeGuru Reviewer
- Identify critical issues, security vulnerabilities, and hard-to-find bugs
- Ex: common coding best practices, resource leaks, security detection, input validation
- Using ML and automated reasoning, supports Java and Python, integrated with GitHub, AWS CodeCommit and BitBucket
CodeGuru Profiler
- Helps understand the runtime behavior of your application
- Ex: too much CPU usage
- Support apps running on AWS or on-premise and minimal overhead of application
AWS Personal Health Dashboard
- Provides alerts and remediation guidance when AWS is experiencing event that affect you
- Alert, remediation, proactive notifications, scheduled activities
Monitoring Summary
- CloudWatch
- Metrics: monitor the performance of AWS service and billing metrics
- Alarms: automate notification, perform EC2 action, notify SNS based on metric
- Logs: collect log files from EC2 instances, lambda functions
- EventBridge: react to events in AWS or trigger a rule on schedule
- CloudTrail: audit API calls made within your AWS account
- CloudTrail Insights: automated analysis of your cloudtrail events
- Amazon CodeGuru: automated code reviews and application performance recommendations
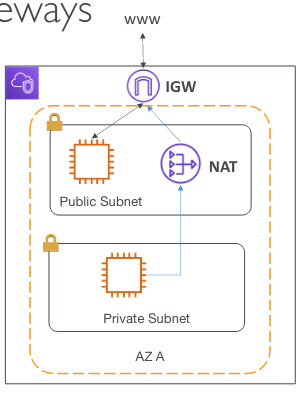
VPC
- Virtual Private Cloud: private network to deploy your resources (regional)
- Subnets: allow you to partition your network inside your VPC (AZ resource)
- Public Subnet: is accessible from the internet
- Private Subnet: is not accessible from the internet
- To define access to the internet and between subnets, we use Route Tables
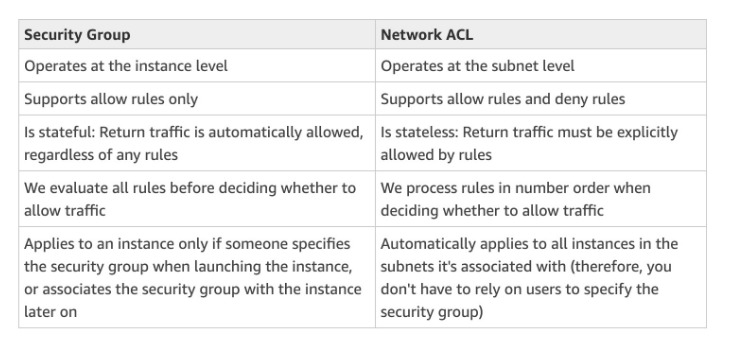
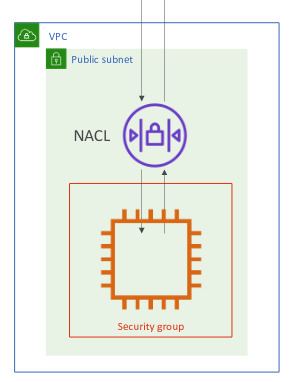
Network ACL and Security Groups
VPC Flow Logs
- Capture Information about IP traffic going into your interfaces
- VPC, Subnet, Elastic Network Interface
- Helps to monitor and troubleshoot connectivity issues
- VPC Flow logs data can go to S3 or CloudWatch Logs
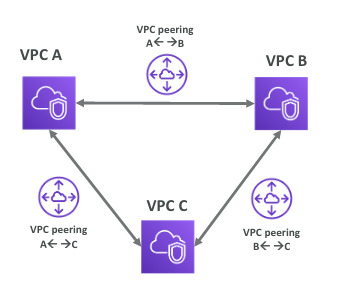
VPC Peering
- Connect two VPC, privately using AWS network
- Make them behave if they were in the same network
- Not transitive, must be established for each VPC that need to communicate
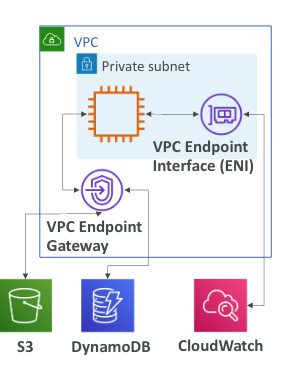
VPC Endpoints
- Allow you to connect to AWS Services using a private network instead of public network
- Enhanced security and low latency
- VPC Endpoint Gateway(S3 and DynamoDB), Interface (the rest)
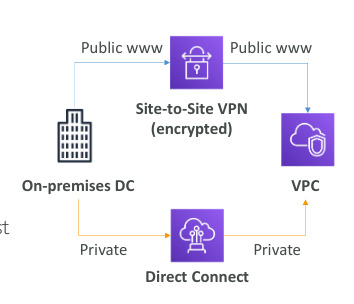
Site to Site VPN & Direct Connect
- Site to site VPN; connect an on-premise VPN to AWS, automatically encrypted, goes over public network Customer Gateway (on-premise), virtual private gateway (AWS)
- Direct Connect(DX): establish physical connection between on-premises and AWS, goes over private network takes a month to establish
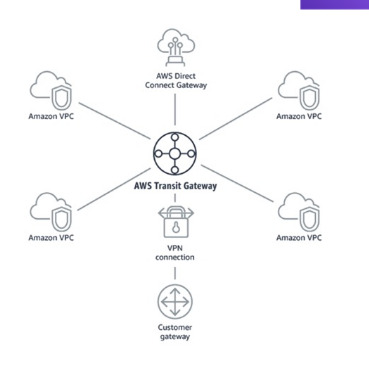
Transit Gateway
- For having transitive peering between thousands of VPC and on-premises
- One single gateway to provide this functionality, works with direct connect gateway, VPN connections
VPC Summary
- Subnets: Tied to an AZ, network partition of the VPC
- Internet Gateway: at the VPC level, provide internet access
- Nat Gateway: give internet to private subnets
- NACL: Stateless, subnet rules for inbound and outbound
- Security Groups: Stateful, operate at the EC2 level or ENI
- VPC peering: connect two VPC with no overlapping IP ranges, no transitive
- VPC Endpoints: Provide private access to AWS Services within VPC
- VPC Flowlogs. network traffic logs
- Site to site VPN: VPN over public network between premises DC and AWS
- Direct Connect: direct private connection to AWS
- Transit Gateway: Connect thousands of VPC and on-premises networks together
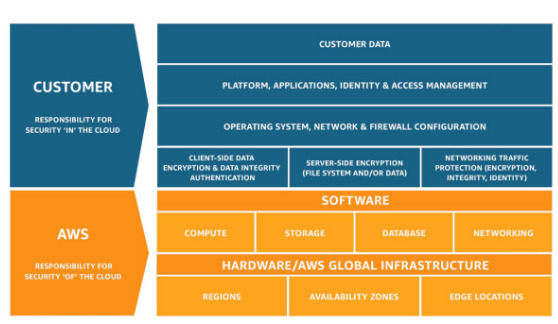
Security & Compliance
- AWS responsibility: Security of the cloud
- Protecting infrastructure
- Managed services like S3, DynamoDB, RDS
- Customer Responsibility: Security in the cloud
- Guest OS(security patches and updates)
- Firewall and network configuration, IAM and encrypting data
- Shared Controls: Patch Management, Configuration management, Awareness & Training
DDOS Protection on AWS
AWS Shield
- AWS Shield Standard: protect against DDoS attack for your website and applications, for all customers at no adittional costs
- AWS Shield Advanced: 24/7 premium DDoS protection (3k usd per month)
- AWS WAF: Filter specific requests based on rules
- CloudFront and Route53: availability protection using global edge network, combined with AWS shield provides solid mitigation at the edge
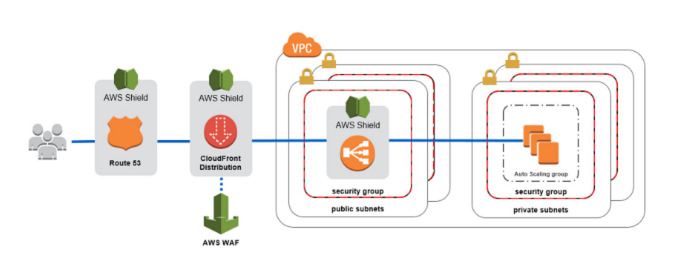
AWS WAF
- Protect your web from common web exploits(Layer 7 http)
- Deploy on Application Load Balancer, API Gateway, Cloudfront
- Define Web ACL (web access control list)
- Rules include IP addresses, HTTP headers, body or URI strings
- Protect from SQL injections, XSS, Block countries, or rate based rules (count occurrences of events) DDos
Pentesting in AWS
- AWS customers are welcome to carry out security assessments against their AWS infrastructure without approval for 8 services:
- Amazon EC2
- Amazon RDS
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon Aurora
- Amazon API Gateway
- AWS Lambda
- Amazon Lightsail resources
- Amazon Elastic Beanstalk
- Prohibited: DNS zone walking, Dos, Port flooding, request flooding, DDos
Encryption
- At rest: data stored archived in device
- Hard disks, RDS service, S3 Glacier Deep archive
- In transit: data being moved from one location to another
- Transfer from on-premises to AWS, EC2 to DynamoDB
- For this we leverage encryption keys
AWS KMS
- Service for encryption: AWS manage the encryption keys for us
- Encryption Opt-in:
- EBS volumes
- S3 buckets: server side encryption of objects
- Redshift database:encryption of data
- RDS database. encryption of data
- EFS drives: encryption of data
- Automatically enabled:
- Cloud trail logs
- S3 Glacier
- Storage Gateway
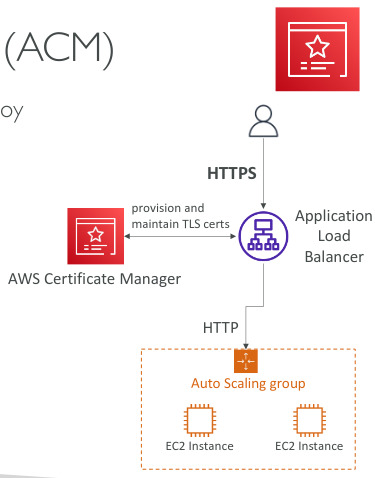
AWS Certificate Manager (ACM)
- Lets you easily provision, manage and deploy SSL/TLS Certificates
- Used to provide in-flight encryption for websites (HTTPS)
- Supports both public and private TLS certificates, free for ublic TLS
- Automatic TLS certificate renewal, integrated with ELB, CloudFonrt, APIs on API Gateway
AWS Secrets Manager
- Newer service, storing secrets, capability to force rotation of secrets every X days
- Automate generation of secrets on rotation (uses lambda)
- Integration with Amazon RDS and are encrypted using KMS
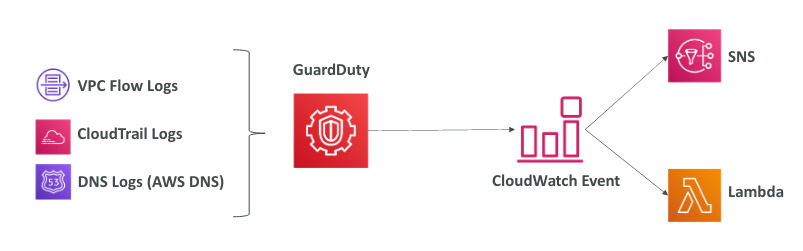
Amazon GuardDuty
- Intelligent threat discovery to protect AWS Account
- Uses ML algorithms, anomaly detection, 3rd party data
- One click to enable (30 days trial), no software to install
- Input data: Cloud trail logs, VPC flow logs, DNS logs
- Can setup CloudWatch Event Rules to be notifies in case of finding targeting AWS lambda or SNS
Amazon Inspector
- Automated Security Assessments for EC2 instances
- Analyze against unintended network accessibility
- AWS Inspector must be installed on OS in EC2 instances
AWS Config
- Helps with auditing and recording compliance of your AWS resources
- Helps record configuration and changes over time
- Questions solved: is there a unrestricted ssh access to my security groups?, do my buckets have any public access?
- You can receive notification in changes, is a per-region service and can be across regions and accounts
Amazon Macie
- Fully managed data security and data privacy service that uses ML and pattern matching to protect your sensitive data in AWS
- Macie helps identify and alert you to sensitive data, such a personally identifiable information (PII)
AWS Security Hub
- Central security tool to manage security across AWS accounts and automate security checks
- Integrated dashboards sowing current security and compliance status to quickly take actions
- Automatically aggregates alerts in predefined findings in:
- GuardDuty, Inspector, Macie, IAM Access, AWS SSM, AWS Firewall, AWS Partner Network Solutions
- Must first enable AWS config service
- GuardDuty, Inspector, Macie, IAM Access, AWS SSM, AWS Firewall, AWS Partner Network Solutions
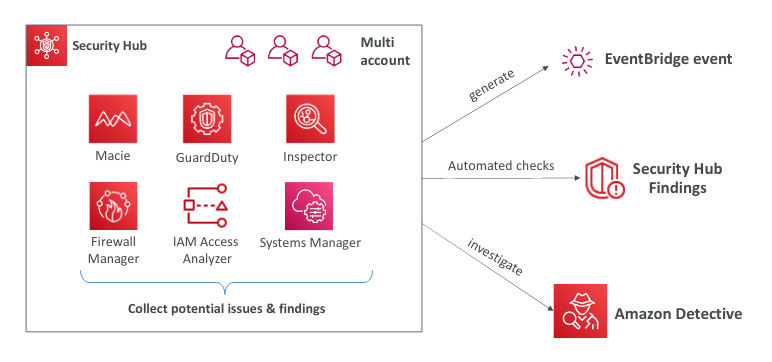
Amazon Detective
- GuardDuty, Macie and Security Hub are used to identify potential security issues or findings
- Analyzes, investigates and quickly identifies the root cause of security issues or suspicious activities( using ML and graphs)
- Automatically collects and processes events from VPC log flows, Cloud Trail, GuardDutiy and create unified view
AWS Abuse
- Report suspected AWS resources used for abusive or illegal purposes
- Spam
- Port Scanning
- Dos or DDoS
- Intrusion attempts
- Hosting copyrighted content
- Distributing malware
- Contact the AWS abuse team
Security & Compliance Summary
- Shield: automatic DDoS protecctions + 24/7 support for advanced
- WAF: firewall to filter incoming requests based on rules
- KMS: Encryption keys managed by AWS
- CloudHSM: Hardware encryption, we manage encryption keys
- AWS Certificate Manager: provision, manage and deploy SSL/TLS Certificates
- Artifact: Get access to compliance reports such as PCI, ISO
- GuardDuty: Find malicious behavior with VPC, DNS and CloudTrail Logs
- Inspector: For EC2 only, find vulnerabilities
- Config: track config changes and compliance against rules
- Macie: Find sensitive data in Amazon S3
- CloudTrail: track API calls by users within account
- AWS Security Hub: Gather security findings from multiple AWS accounts
- Amazon Detective: Report AWS resources for abusive or illegal purposes
- Root user privileges: change account settings, close AWS account, change or cancel AWS support plan, register as a seller in marketplace
Account Management, Billing, Support
AWS Organizations
- Global services, allows to manage multiple AWS accounts
- Consolidated billing across all accounts
- Pricing benefits from aggregated usage (discounts for EC2)
- API available to automate AWS account creation
- Restrict account privileges using Service Control Policies (SCP)
- Create accounts per department, per cost center, for better isolation
- Use tagging standard for billing purposes, enable CloudTrail and CloudWatch log to send to central S3 account
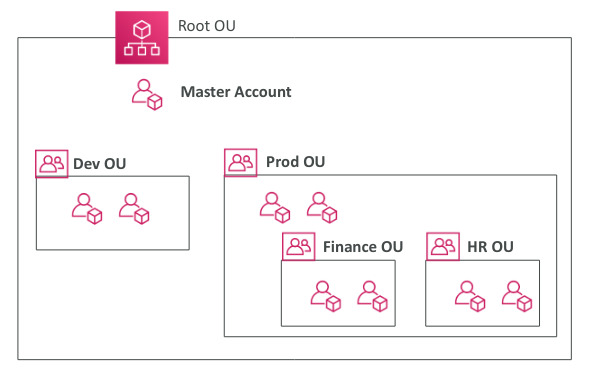
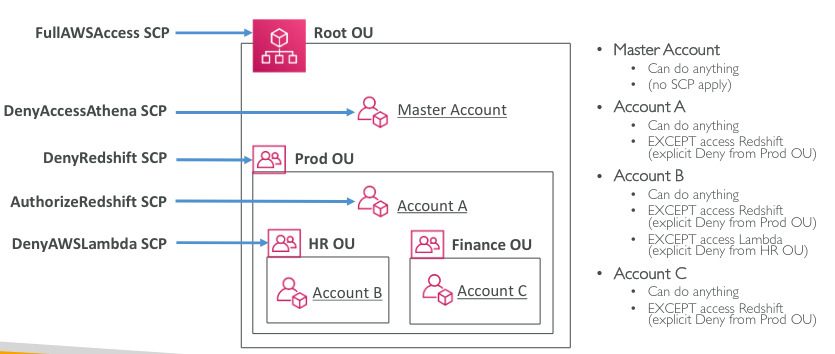
Service Control Policies (SCP)
- Whitelist or blacklist IAM action
- Applied at the OU or Account level
- Does not apply to the master account
- SCP must have an explicit Allow(does not allow anything by default)
- Restrict access to certain services, enforce PCI compliance by explicitly disabling services)
AWS Consolidated Billing
- Combined Usage:combine the usage across all AWS accounts in AWS Organization to share the volume, pricing and saving plans discounts
- One Bill : get one bill for all AWS accounts in the org
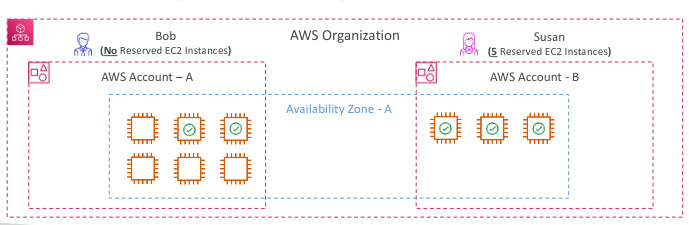
- The management account can turn off Reserved Instances discount sharing for any account in the AWS Organization, including itself
AWS Control Tower
- Easy way to set up and govern a secure and compliant multi-account AWS environment based on best practices
- Automate the set up of your environment in few clicks
- Automate ongoing policy management using guardrails
- Monitor compliance through an interactive dashboard
- AWS Control tower run on top of AWS Organizations, so work with this service
Pricing Models in AWS
- Pay as you go: pay for what you use, remain agile, meet scale demands
- Save when you reserve: minimize risks, comply with long term requirements, EC2, DynamoDB,RDS…
- Pay less by using more: volume-based discounts
- Pay less as AWS grows
Free tier services
- IAM
- VPC
- Consolidated billing
- Elastic Beanstalk
- Cloud formation
- Auto scaling groups
Compute Pricing Services
EC2
- On demand instances: minimun of 60s, pay per second (win/linux) or per hour(other)
- Reserved instances: up to 75% discount, on demand hourly rate, 1-3 year commitment, all upfront, partial, no
- Spot instances: up to 90% discount, bid for unused capacity, have risks
- Dedicated Hosts: on-demand, reservation for 1 or 3 years
- Savings plans as an alternative to save on sustained usage
Lambda
- Pay per call
- Pay per duration
ECS
- EC2 launch type model: no additional fees
- Pay for AWS resources stored and created in your application
Fargate
- Pay for vCPU and memory resources allocated to your applications in your containers
S3
- Storage class, number and size of objects
- Number and type of requests
- Data transfer OUT the S3 region, S3 transfer acceleration
- Similar to EFS (lifecycle rules)
EBS
- Volume type(based on performance)
- Storage volume in GB per month
- IOPS, Snapshots, Data transfer (inbound is free)
RDS
- Per hour billing
- Engine, size, memory class
- Purchase type: on demand, reserved instances (1 or 3 years) with required up-front
- No additional charge for backup storage
- Number of input and output requests per month, Deployment type: single AZ, multiple AZs
CloudFront
- Pricing is different across regions
- Aggregated for each edge location, then applied to your bill
- Data transfer out (volume discount), number of https requests
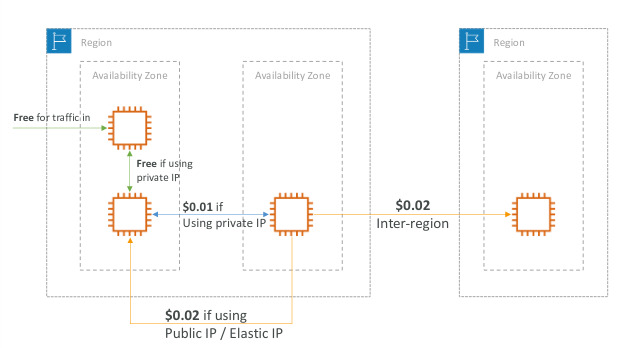
- Using private IP instead of public ip for good saving and network performance between EC2
- Use same AZ for maximum savings ( at the cost of high availability)
Saving Plan
- Commit a certain $ amount per hour for 1-3 years
- EC2 Saving Plan
- Up to %72 discount compared to On-Demand
- Commit to usage of individual instance families in a region
- Compute Saving Plan
- Up to 66% discount compared to on-demand
- Regardless of family, region, size, os, tenancy, compute options
- EC2, Fargate, Lambda
- Setup in the AWS Cost Explorer console
AWS Compute Optimizer
- Reduce costs and improve performance by recommending optimal AWS resources
- Use ML to analyze your resources and their utilization CloudWatch metrics
- Supported resources: EC2 instances, EC2 Auto scaling groups, EBS volumes, Lambda functions
- Lower your cost up to 25%, recommendation can be exported to S3
Billing and Costing Tool
Estimating costs in the cloud
- TCO Calculator: estimate costs saving, comparing on-premise to aws cloud, ideal for executive presentations
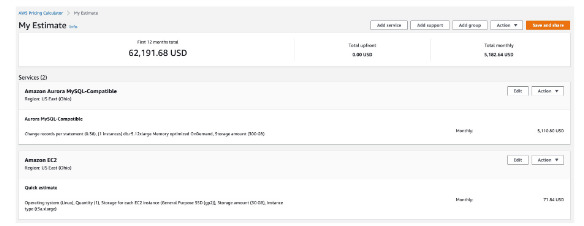
- Simply monthly calculator /pricing calculator: AWS Pricing Calculator, estimate cost for your architecture solution
Tracking costs in the cloud
- Billing dashboard: high level tool, show free tier
- Cost allocation tags: use cost allocation tags to track your AWS cost on detailed level (AWS generated or user defined), used for organizing resources for departments
- Cost usages reports: dive deeper into your AWS costs, most comprehensive set of AWS cost and usage, can be integrated with Athena, Redshift and QuickSight
- Cost explorer: visualize, understand and manage your AWS cost, create custom reports, analyze your data at high level, choose an optimal Saving plan, forecast usage up to 12 months
Monitoring against costs plan
- Billing alarms: data metric in Cloud Watch is stored in us-east-1, its for actual costs,not projected costs, intended a simple alarm, not powerful as AWS Budgets
Budgets: send alarms when costs exceed the budget, 3 types: usage, costs, reservations
Up to 5 SNS notifications per budget, 2 budgets are free, then 0.02 per day or budget
AWS Trusted Advisor
- No need install anything, high level AWS assessment
- Analyze AWS accounts and provides recommendation on 5 categories:
- Cost optimization
- Performance
- Security
- Fault tolerance
- Service Limits
Support Plans
- 7 core checks for Basic and Developer plans
- S3 bucket permissions
- Security Groups: specific ports unrestricted
- IAM Use
- MFA on root Account
- EBS Public snapshots
- RDS Public snapshots
- Service limits
- Full checks for Business and Enterprise Support plans
- Full checks available on the 5 categories
- Ability to set CloudWatch alarms when reaching limits
- Programmatic Access using AWS support API
AWS Basic Support Plan
- Customer service and communities : 24/7 access to customer service, documentation, whitepapers and support forums
- AWS Trusted advisor: 7 core trusted advisor checks
- AWS personal Health Dashboard: personalized view of health of AWS services
AWS Developer Support Plan
- All Basic Support Plan
- Business hours email access to Cloud Support
- Unlimited cases - 1 primary contact
- General guidance < 24 business hours
- System impaired < 12 business hours
AWS Business Support Plan (24/7)
- Intended to use if you have production workloads
- Trusted advisor - full set of checks + API access
- 24x7 phone, email and chat access to Cloud Support Engineers
- Unlimited cases - unlimited contacts
- Production system impaired < 4 hours
- Production system down < 1 hour
AWS Enterprise Support Plan (24/7)
- Intended to use if you have mission critical workloads
- Access to a Technical Account Manager (TAM)
- Concierge Support Team
- Infrastructure Event Management, Well Architected and Operations Reviews
- Business-critical system down < 15 minutes
Account Best Practices - Summary
- Operate multiple accounts using Organizations
- Use SCP to restrict account power
- Easily setup multiple account with best-practices with AWS Control Tower
- Use tags and Cost Allocation Tags for easy management and billing
- IAM guidelines: MFA, least-privilege, password policy, password rotation
- Config to record all resources configurations and compliance over time
- CloudFormation to deploy stacks across accounts and regions
- Trusted Advisor to get insights, Support Plan adapted to your need
- Send service Logs and Access Logs to S3 or CloudWatch Logs
- CloudTrail to record API calls made within your account
- If yout Account is compromised: change the root password, delete and rotate all the passwords, contact AWS support
Billing and Costing Tool - Summary
- Compute Optimizer: recommends resources configuration to reduce cost
- TCO Calculator: from on-premise to AWS
- Simple Monthly Calculator : cost of service on AWS
- Billing dashboard: high level overview + free tier dashboard
- Cost Allocation Tags: tag resources to create detailed reports
- Cost and Usage reports: most comprehensive billing dataset
- Cost explorer: View current usage (detailed) and forecast usage
- Billing alarms: in us-east-1 track overall and per-service billing
- Budgets: more advances - track usage, costs, RI, and get alerts
- Savings Plans: easy way to save based on long-terms usage of AWS
Advances Identity
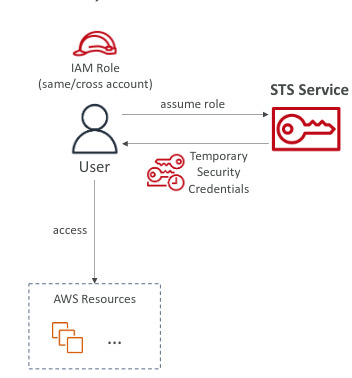
AWS STS (Security Token Service)
- Enables to create temporary, limited-privileges credentials to access your AWS resources
- Short-term credential: you configure expiration period
- Use cases: Identity federation, IAM Roles for cross accounts, IAM roles for EC2
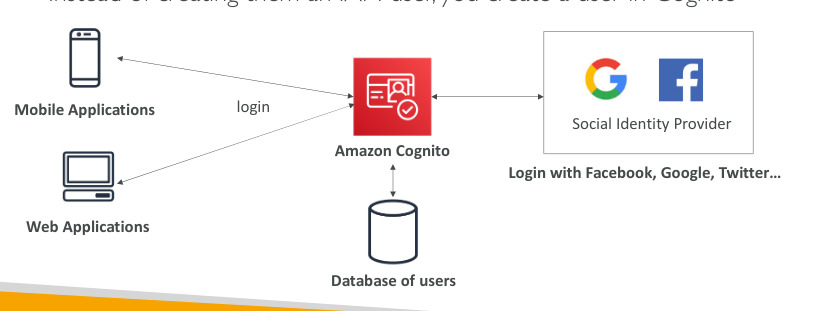
Amazon Cognito (simplified)
- Identify for your Web and Mobile applications users (potentially millions)
- Instead of creating them an IAM user; your create a user in Cognito
Microsoft Active Directory (AD)
- Found on any Windows Server with AD Domain Services
- Database of objects: User Accounts, Computers, Printers, File shares, Security Groups
- Centralized security management, create account, assign permissions
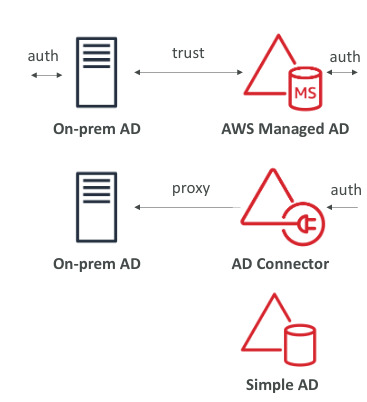
AWS Managed Microsoft AD
- Create your own AD in AWS, manage users locally, support MFA
- Establish ‘trust’ connections with your on-premise AD
AD Connector
- Director Gateway to redirect to on premise AD
- Users are managed on the on-premise AD
Simple AD
- AD-compatible managed directory on AWS
- Cannot be joined with on-premise AD
AWS Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Use on-login to access multiple account and 3er party applications
- Integrated with AWS Organizations and on-premise AS
- Supports SAML 2.0 markup
Advanced Identity - Summary
- IAM: Identity Access Management, used for users that you trust and belong to your company
- Organizations: Manage multiple AWS accounts
- Security Token Service (STS): temporary, limited privileges credentials to access AWS resources
- Cognito: create a database of users for your mobile and web applications
- Directory Services: integrate Microsoft Active Directory in AWS
- Single Sign On (SSO): one login for multiple AWS accounts and applications
AWS Well Architected Framework
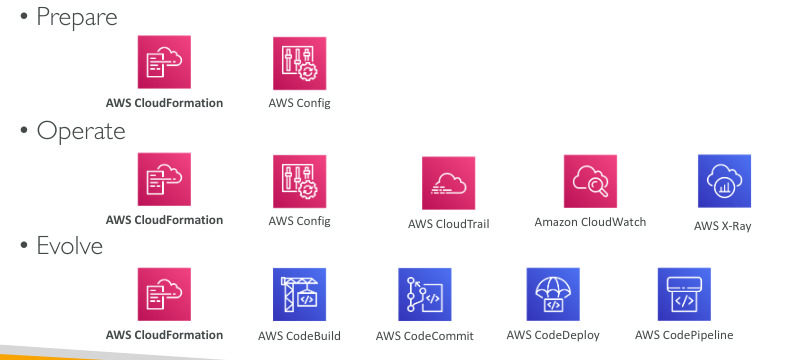
Operational Excellence
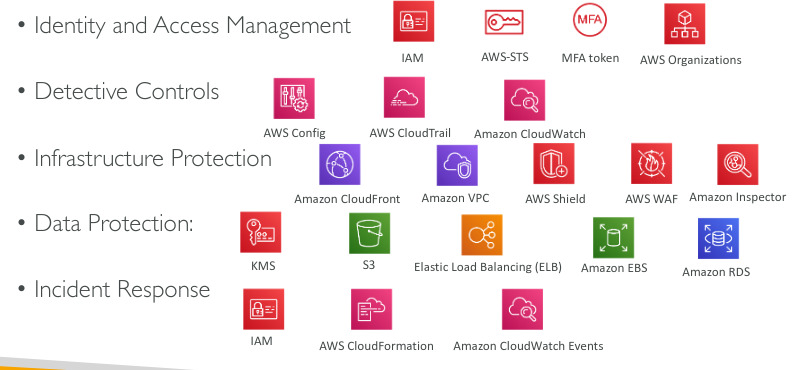
Security
Reliability

Performance Efficiency

Cost Optimization