Cloud Concepts
Benefits of cloud computing
Scalability: ability to accommodate a larger load by making the hardware stronger(vertical), or by adding nodes (horizontal)
Elasticity: once a system is scalable, elasticity mean that there will be ‘auto scaling’, based on the load, this is cloud friendly : pay per use, match, optimize costs
Agility: (not related to scalability), new IT resources are only a click away, it mean that you reduce the time to make those resources available to your developers from weeks to minutes
Availability: goes in hand with horizontal scaling, mean running your application at least in 2 availability zones, the goal is to survive a data center loss (disaster)
Differences between CapEx and OpEx and Consumption-based model
Capital Expenditure (on-premise): Purchasing some assets upfront (servers) and I need to use for a certain time Operational Expenditure (the cloud): Consumption by the pay for what i use as i am use it, gives flexibility
A consumption-based pricing model is a service provision and payment scheme in which the customer pays according to the resources used. This model is essentially the same as the utility computing payment structure and those of other utilities, such as water and electricity.
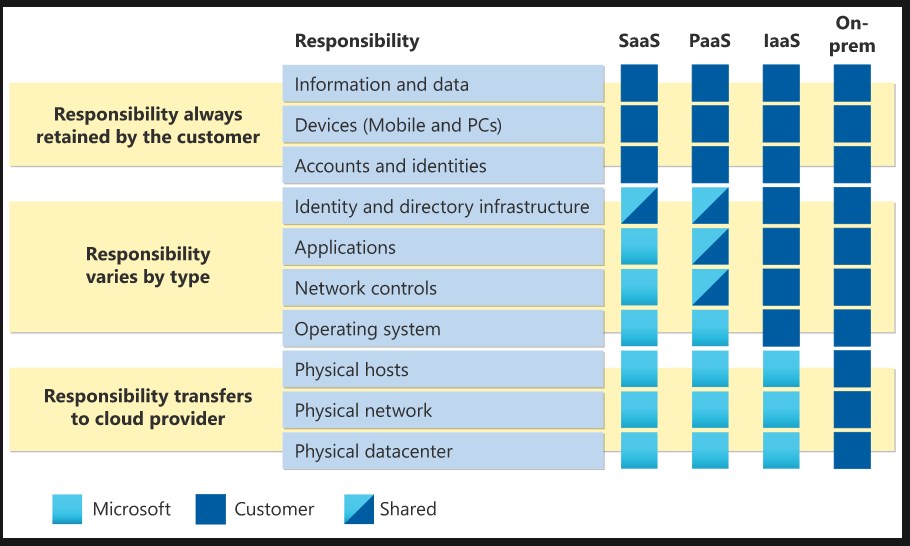
Differences between categories of cloud services
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Provide building blocks for cloud IT
- Provide networking, computers, data storage space
- Highest level of flexibility
- Simulate the look from managing physical resources
- Eg: VMs, Blob Storage, GCP, Digital Ocean, Elastic Load Balancing
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Remove the company to manage underlying infrastructure
- Focus on deployment and management of applications
- You will define the behavior and environment for your application (code)
- Eg: Heroku, EKS, ACI
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Completed product that is run and managed by the service provider
- offer services meant to be accessed by end users
- Eg: Gmail, Outlook, Recognition for ML, Zoom
Shared Responsibility model:
Differences between types of cloud computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. You typically pay only for cloud services you use, helping you lower your operating costs, run your infrastructure more efficiently, and scale as your business needs change.
- Public Cloud: Limitless, many regions, over internet, like Azure, AWS or GCP
- Hybrid Cloud: We are using both, like provide some services from my servers and in busy days provide from the cloud
- Private Cloud: Management of servers, more customizable, we can bring azure capabilities on premise with Azure Stack and Azure arc
Azure Core Services
Core Azure Architectural Components
Region
A region is a group of data centers that interact to provide redundancy and availability for the services hosted within that region. For example, West US, Central US and North Central US are three of many regions, each one is paired with another in the same geography to allow replication of resources and reduce data loss. Microsoft establishes and controls the pairing of regions, you cannot choose a region pair, however you choose the region in which deploy a service, which indirectly determines which other region is in the pair.
Availability Zones
They area data centers that are grouped in regions with low latency connection, we can pick up to 3 AZ when deploying a service, there are no correlation between buildings and subscriptions.
Azure availability zones-enabled services are designed to provide the right level of resiliency and flexibility. They can be configured in two ways. They can be either zone redundant, with automatic replication across zones, or zonal, with instances pinned to a specific zone. You can also combine these approaches.
Some organizations require high availability of availability zones and protection from large-scale phenomena and regional disasters. Azure regions are designed to offer protection against localized disasters with availability zones and protection from regional or large geography disasters with disaster recovery, by making use of another region.
Resource Groups
Like a logical container for your resources, you can apply various properties to the resource group and those properties apply to all the resources in that resource group, keep in mind these list when create resource group:
- Lifecycle: All resources should share the same lifecycle for deployment, updates and deletion
- Resource Assignment: A resource can exist in only one group, but you can add or remove a resource to or from the group as needed. You can also move resources from one group to another.
- Resource Interaction: resources from different resource groups can interact each other
- Deletion: When you delete a resource group, all resources in the group are deleted
- Creation: You can use Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI or an Azure resource manager template to create a resource group
- Tags: You can apply tags to a resource group to differentiate areas in your organization, the tag applies only to the resource group and not the resources inside the group, think like is only a label of the resource group, however you can put tags in the resources inside
- A resource group can contain resources from any region, not just the region in which the resource group is located
Azure Subscription
A resource group serves as a logical container for resources, Azure Subscriptions serves the same but a higher level, like a box that contains all your resource group boxes, also a resource group only exist in one subscription.
Azure Subscriptions can serve as:
- Administrative boundaries (control security, resources and policies)
- Payment Agreement, ex: pay-as-you-go offer tied to a credit card billing each month
- Legal Agreement with specific Azure plan, each with its own rate plan, terms and conditions ex: free trial
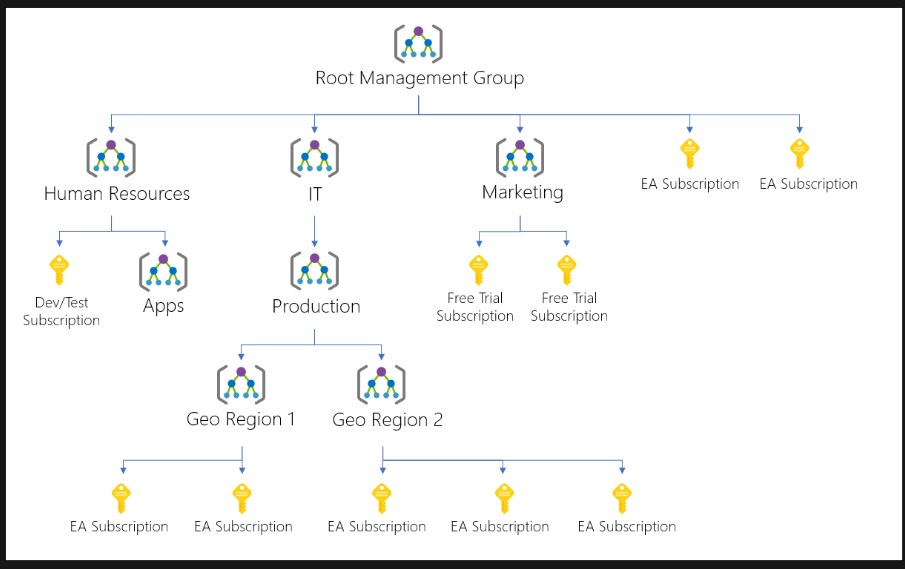
Management Groups
- Useful for managing access, policies and compliance for your subscriptions
- Level of scope above subscriptions
- Use case: limit regions available for VMs creations
Hierarchy of management groups and subscriptions
Resource Manager
- Everything in azure is a resource (vm,db,etc..)
- Useful for manage resources, serving as a deployment service for azure
- ARM support use of templates to create, manage resources in JSON format
- You can automate the deployment of an entire Azure environment by using templates, only need to declare what you want to create and the properties, and the ARM passes that information to Azure providers
Core Azure Services
Virtual Machines (IaaS)
- Full control over OS
- Maintain and patch VM image
- Has scalability, flexibility
- You can move from host to host due to the metadata that defines the VM
Virtual machine scale sets
- Simplify the creation and managing a group of load-balanced VMs
- Scale in or scale out to adjust the demand
- Enables high availability in themselves (up to 1000 VMs or 600 custom images)
- Created from the same OS image (same applications and config)
- You can use AZs to further improve availability by distributing the VMs across multiple data centers
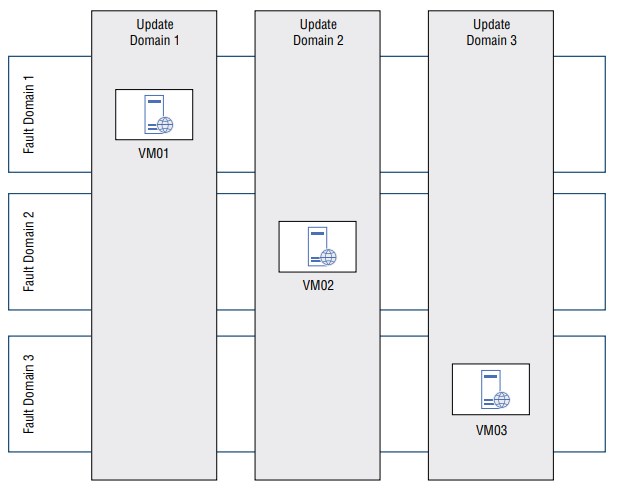
Availability Set
- Help avoid potential outages caused by hardware issues and update VMs without causing the set to be unavailable
- Fault Domain: Group of hardware that shares a power source and network switch, similar to a rack
- Update Domain: Group of hardware thar undergoes maintenance activities or reboot events at the same time
- Availability sets distributes VMs across multiple fault domains and update domains
![]()
Azure App Service
- PaaS Service that enables quickly develop and deploy web apps
- Support .net, java, ruby, python, etc.. and Windows or Linux OS and docker containers
- Offers load balancing, autoscaling, automated management(updates), security features and templates from Marketplace
Azure Container Instances (ACI)
- Offers the fastest and simples way to run a container in Azure is a PaaS service where you upload your container and runs for you
- Cost saving because you are only paying for consumption of CPU and memory used by container, rather than paying a VM
- Serves as a virtual environment that includes the resources necessary for its hosted application to function
- Designed to be created, scaled out and stopped dynamically
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- AKS is a container orchestration service that monitors health
- Provides scalability and resource sharing among container in a Kubernetes cluster
- This service is a complete orchestration for containers with distributed architectures and large volume, can use the same image for deploying
Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD)
- Enables your users to use a cloud-hosted version of Windows from any location
- Azure Virtual Desktop works across devices like Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and Linux
- Good for users working from home, rather than provision a new Windows device
- Provide best user experience, enhance security, simplified management performance management and multi-session win 10 enterprise deployment
Core Azure Storage
Blob Storage
- Optimized to store large amount of unstructured data
- Accessed through HTTP or HTTPS, Azure Storage API, Azure Powershell, Azure CLI or Azure storage client library
- Similar to S3 from Amazon Web Services
- Tiers:
- Hot access: Optimized for storing frequently accessed data
- Cool access: Optimized for data you access infrequently or for a relatively limited period of time
- Archive access: Data that you rarely access, ex:long-term storage backups
- Hot an cool stores data online, but cool means lowe storage cost but higher access cost
Disk Storage
- Attached to a VM, like a physical disk in a server, 99.999 availability through replicas
- Offer three main types: data disk, OS disk and temporary disk
- OS and data disks are persistent, they don’t go when you reboot your VM
- Support server-side-encryption and disk encryption
- Server-side-encryption is enabled by default with bitlocker(Windows) and DM-Crypt(Linux), meet compliance and policy requirements
- Disk encryption enables you to encrypt OS and data disks
File Storage
- Files that are available from anywhere in the world but not associated with a VM or volume letter
- Can be accessed by Server Massage Block (SMB) or Network File System (NFS)
- Used for replacing existing data on premise file servers, moving data from on-premise to Azure and sharing data required by apps
Storage Accounts
- Before you use storage in Azure you must create an storage account, this account provides an unique name through which you can access these objects via HTTP or HTTPS
- Types of account:
- General-purpose v1: Legacy account type intended for blobs, files, queues and tables
- General-purpose v2: Intended for blobs, files, queues as well as Data lake Gen2
- BlockBlobStorage: Intended for block blobs and append blocs in high-performance such as high transaction rates and for low latency
- FileStorage: Intended for files-only storage scenarios where premium performance is required
- BlobStorage: Legacy blob-only storage account type
Core Data Services
SQL Server on Azure VMs
- Good for fast migration of SQL server from on-premise to Azure with retention of operating system access
- Enables lift-and-shift from an on-premise datacenter to Azure with ease, while maintaining compatibility
Azure SQL Database
- You should use this solution for Cost-effective, serverless database with an intermittent usage pattern and a low compute utilization over time
- Abstracts all the infrastructure needed to host a SQL database
- Is a PaaS in which Microsoft manages maintenance like upgrades, patching and monitoring to ensure 99.99 uptime
- You only focus on creating the SQL database and managing tables, views, etc
Azure SQL Managed Instances
- Is a PaaS service that provides scalable cloud data service without need to deploy hardware
- Enables frictionless migration to Azure with minimal application and database changes, at the same time it eliminates overhead for the management of underlying infrastructure
- Differences with azure SQL
- SQL MI offers features for auditing, authentication, backups,
- change data capture (CDC)
- common languaGe runtime (CLR)
- linked servers, OPENQUERY…
- Can integrate with the Azure Data Migration Server, enable easy move from on-premise to Azure managed instance
Cosmos DB
- Multimodel Database: scale data out to multiple Azure regions in the globe
- Provides excellent elasticity in both throughput and storage, good for peak hours
- Supports SQL and NoSQL databases like MongoDB, Cassandra, Gremlin API (massive graphs)
Azure Database for MySQL
- Serverless service, only focus on your MySQL databases without worrying about the infrastructure
- If you see the LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) stack for development in the exam think about MySQL
Azure Database for PostgreSQL
- PaaS service, support PostgreSQL database engine with scalability, elasticity, high availability and more
- PostgreSQL is appropriate in situations where you want to deploy and manage PostgreSQL databases without worrying about underlying infrastructure
Azure Database Migration Service
- Supports variety of database migrating scenarios for offline and online migrations
- Offline occurs when the resource is not in use
- In an online migration the data is synchronized from the live source to the target and then the app is cut over the new instance of the database
Core Networking Services
Virtual Networks
- VNet enables virtual machines and other services to communicate among themselves, with the internet and with your on-premise network
- VNets adds availability and scalability to your network resources in Azure
- When you create a VNet you specify the private IP adress space that the VNet will use
- VNets are scoped to a single region and subscription but span in all AZs in each region
- You can use virtual network peering to connect VNet across regions with the same latency if they where on the same virtual network
Load Balancers
- Distribute network traffic across multiple resources to improve responsiveness, reliability and availability
- Azure offer four load balancing services:
- Azure Front Door:
- Designed for global or multiregion routing and site acceleration, uses the Microsoft global edge network to enable fast, secure and scalable web applications
- Support URL path based like application gateway, but this is globally distributed (caching, high availability, fast failover)
- Azure Traffic Manager:
- Is an application layer DNS-based traffic that balances traffic at the domain level across global Azure regions, offers options for routing and detecting point health
- Appropriate for DNS-based global routing, detecting endpoint health and routes traffic to the data center closest to the users
- Azure Application Gateway:
- Provides application delivery controller (ADC) as a service, applicable for HTTPS traffic and can route traffic based on incoming URL, URI path, and host headers
- Good for HTTP(S) traffic, for example when the URL includes videos in the path and you want to direct traffic to a set of web servers
- Azure Load Balancer
- Is a transport layer service designed for high performance and low latency, support zone-redundant and applies for non HTTP(S) traffic
- Good for balancing traffic among multiple database VMs
- Azure Front Door:
Azure VPN Gateway
- VPN establishes an encrypted tunnel between two private networks across public network
- For example: you can establish a secure connection between your on-premise network and your resources in azure
- Supports multiple VPN configurations:
- Site-to-site: Establishes a VPN between two sites, such as between your on premise data center and azure
- Multi-site: Establishes VPN tunnels between azure and multiple on-premise sites
- Point-to-site: Establishes a VPN tunnel from a single device (point) to a site
- VNet-to-VNet: Establish a VPN between two Azure VNets
ExpressRoute
- Create private connection between Azure Datacenters and infrastructure on premise (cost saving)
- Don’t go over the public internet, and offer more reliability, faster speeds, and lower latencies than typical internet connections
Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
- Places web content across networks to make readily available to users on their location
- Example: If a user in USA want to see a video that you host in Italy, you could place those files in CDN that has a point of presence in Virginia, when the user access this file, the file come from the cached copies in the CDN, rather than your server in Italy
- Each file has a time-to-live (TTL) property that determines when the file should be refreshed from the source to the cache
Summary
- Networking Addressing: Devices on a network are assigned a network address, subnets create virtual networks to segregate devices within an address space, when you create a resource you specify the address segment and the IP (static or dynamic)
- Routing: Routers move network traffic between network segments, make possible to communicate between public networks and private networks with public ones
- Domain Name Service (DNS): Provides a hots-to-address resolution, enabling application to determine the IP address associated with a hostname
- Virtual Private Network: Creates an encrypted tunnel between two private networks across public networks
- Load Balancer: Distributes traffic to a group of servers or services, enabling the load to be shared among them, and enables fault tolerance
- Express Route: Establish a secure VPN connection bypassing the internet, connects directly to the Microsoft global network
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): CDN places content near users and reduce network traffic and latency
Core Solutions and Management Tools
Internet of Things (IoT)
Azure IoT Hub
- Azure-hosted service that server as message hub between IoT devices and Azure services
- Requires you to write code to connect IoT devices
- Supports multiple protocols, SDK, highly scalable which means it can integrate billions of devices
- Support multiple communication and control functions, including:
- Device-to-cloud telemetry to collect data
- Device-to-cloud file upload to collect and transfer data
- Request/reply methods for controlling devices from the cloud
- Monitoring
- IoT hub can route messages received to other Azure services
- Can not support analyzing of telemetry data
Azure IoT Central
- SaaS solution to build IoT solutions without development expertise
- Builds on the functions provides by IoT Hub to provide dashboards for control, management features
- You can connect new devices, view telemetry, view overall device and create alerts to notify you
- You can use device templates, which allow you to connect new devices without any coding in IoT central
- This solution supports device-to-cloud messaging and per-devide identity
Azure Sphere
- Integrated IoT solution that consist of three key parts:
- Azure Sphere micro controller unit (MCUs): Hardware component built in the IoT device
- Management software: Custom linux OS that manages communication with security service
- Azure Sphere Security Service (AS3): Handles certificate-based device auth to Azure, updates the software to prevent vulnerabilities in the device
Data Analytics
Data Lake Analytics
- Big Data solutions that allows developers to write code with a mixture of SQL and C# syntax, the language is called U-SQL
- Allows developers to user their existing skills to process data a large-scale
Azure Synapse Analytics
- Good if you are looking for distributed query solution, that works with machine learning
- Offers serverless and dedicated resource model, requires the use of five different application components which forms an Azure Synapse cluster
HDInsight
- Managed Apache Hadoop service that lets you run Apache Spark, Hive, Kafka, HBase and more (big data)
- Makes ease, fast and cost effective to process massive amounts of data in a customizable environment
- Some of its capabilities are:
- Cloud Native
- Low-cost and scalable
- Secure and Compliant
- Monitoring
- Global, productivity
Azure Databricks
- Is an Apache Spark based analytics platform designed to provide collaborative analytics workflow
- Data analytics platform optimized for Azure, offers three environments for developing apps:
- Databricks SQL: easy-to-use platform, run SQL queries on their data lake, build and share dashboards
- Databricks Data Science & Engineering: enables collaboration, for big data pipelines, can work with apache kafka and IoT hub, Spark
- Databricks Machine Learning: integrated end-to-end ML environment with managed services for experiment tracking, model training, feature development and model serving
Azure Event Hub
- PaaS service offering that can ingest and process millions of events per second from websites, mobile apps, and IoT devices
- It can be part of big data streaming or feed a real time analytics solution
Azure Stream Analytics
- PaaS solution designed to process high volumes of fast streamed data from sources like sensors, IoT devices and apps
- Identify patterns and relationships in the streamed data to trigger actions, initiate workflows, feed reporting tools and redirect data to storage solutions
Artificial Intelligence
Azure Machine Learning
- Through testing you determine the model that provide the most accurate predictions
- Can use Machine Learning Studio (portal web) for create no-code solutions using a selection of tools (drag-and-drop), also manage assets and resources
- You should use Machine Learning service when you want to create machine learning algorithms by using python, there are thousands of open-source Python packages with machine learning components
- Machine Learning Studio allows you to use built-in algorithms, not write custom algorithm in python
Azure Cognitive Services
- Provide ML models designed to interact with humans and execute cognitive function that humans would normally do, the following list summarizes the services:
- Language: To process natural language to determine, for ex: the user question or sentiment
- Speech: Convert speech into text or text into speech, can translate one language to another, recognize and verify the speaker
- Vision: Provides identification for analyzing images, videos and similar visual data
- Decision: Personalize user experience with recommendations, remove offensive content…
Azure Bot Service
- Enables you to create virtual agents to interact with users
- Answer questions, get information and start activities with other azure services
- Can use all the cognitive services to do activities like understand what user is asking
Azure Marketplace
- Provides purchase and subscriptions links to certified cloud applications and solutions from Microsoft and its technology partners
- All solutions offered are certified through the Microsoft Azure Certification Program
- This ensures compatibility with the Azure public cloud
- Offerings include:
Azure Function
- If you used AWS, is similar to Lambda function, enables you to host a single method that runs in response to an event
- You can use different programming languages to code this function
- Scales automatically, pay only for the time and resources needed while function is running
- Is stateless, does not store it state from every execution, executes the same every time
- Excellent solution for building small blocks of code that run for a very short time in response to an event
Azure Logic Apps
- More complex than a function, like a workflow, create no-code and low-code solutions to automate and orchestrate tasks, business processes and workflows
- Build the apps using web-based design environment by connecting triggers to actions with various connections, ex: a message arriving a queue is a trigger, this event pass the massage to other service
- Priced based on the number of executions and the type of connectors that the app uses
Azure Event Grid
- Provides solution for building event-driven architectures that subscribe to Azure resources and route events for different endpoints
- Event grid can subscribe to a variety of Azure resources including storage resources, resource groups and IoT Hubs
- Events can be filtered before being forwarded to appropriate event handlers for processing
DevOps
Azure DevOps Services
- Is a group of services that enables and support multiple stages in development process, include the following:
- Azure Artifacts: Repository for storing development artifacts such as compiled source code
- Azure Boards: Manage individuals items, task, features and bugs
- Azure Pipelines: Automatically build and test code projects
- Azure Repos: Source code repository for collaborating on development projects
- Azure Test Plans: Automated testing tool for code
Github Actions
- Offers many of the same functions as Azure DevOps
- Github is the appropriate choice for collaborating on open source projects and DevOps is the appropriate choice for enterprise/internal projects
Azure DevTest Labs
- Automates deployment, configuration and decommissioning of VMs and Azure resources
- You can decommission all those services so that you pay only for the resources you need for testing while your are testing them
- Can use ARM templates to deploy any type of resource, however DevTest Labs does not provide monitoring, alerting or telemetry services to monitor those resources
Azure Management Tools
Azure Portal
- Web interface that enables you ti view, create and manage Azure resources and services
- Easy to use because it offers a familiar web-based user experience, also provides a wealth of visualization tools and reports
- You can encounter dashboards, blade or resource panel
- A blade is a panel that slides out in a navigation sequence, it represents a single level navigation hierarchy, each blade provides either information or configuration option
- A dashboard is a collection of customizable tiles that are displayed in the portal, you can add remove and reposition tiles as you wish
- A resource panel is the left-most panel in the portal, is lists the main resource types that are available
Azure PowerShell
- Scripting environment to execute commands to perform management tasks in Azure through Azure REST API
- Those scripts can be simple or complex, potentially deploying hundreds of resources in short period
- You can access powershell through Azure Cloud shell
Azure CLI
- If you are experienced with Bash, this is your best option, is a driven scripting environment that also uses REST API
- You can access via web browser through the Azure Cloud Shell
Azure Cloud Shell
- Web based interface that enables you to run Azure PowerShell, Bash and Azure CLI commands and scripts
- A storage account is required to use Azure Cloud Shell
Azure Mobile App
- Enables you to manage Azure resources from your mobile device
- Is not great management solution for complex tasks, but you can do basic functions with your apps like reset a web app
Azure Advisor
- Personalized cloud consultant that helps you follow best practices to optimize your Azure deployments
- Analyzes your resource configuration and usage telemetry to give the best recommendations
- Gives you recommendation based on:
- Operational Excellence
- Security
- Reliability
- Performance efficiency
- Cost Optimization
Azure Monitor
- Helps you maximize the availability and performance of your apps and services
- Collect, analyze and acting on telemetry from your cloud and on-premise environments to understand how your apps are performing and identify issues affecting them and the resources they depend on
- With Azure Monitor you can:
- Detect issues across applications and dependencies
- Drill into your monitoring data for troubleshooting
- Create visualizations with azure dashboards
- Create actions that execute automatically in response to alerts
Azure Service Health
- Keep you informed about the health of your cloud resources
- Include current and upcoming issues such as service impacting events, planned maintenance, …
- Combination of three separate smaller services
- Status page: Provides information on Azure services globally to help you see at a glance what services are affected in what regions
- Service Health: Gives you information about service issues, planned maintenance, health advisories, and security advisories in a dashboard
- Resource Health: Tracks the state of the resources you have deployed to Azure to give you visibility to any ongoing or historical issues with those resources
General and Network Security
Azure Security
Azure Security Center
Monitoring service that provides threat protection across both azure and on-premise datacenters
- Support Windows and Linux OS
- Integrates natively with Microsoft Defender to provide risk detection and assessment with threat intelligence
- Provide security recommendations
- Detect and block malware
- Analyze and identify potential attacks
- Just-in-time access control for ports
- Capabilities:
- Policy Compliance
- Continuous assessments
- Tailored recommendations
- Threat protection
Azure Sentinel
- Security information management (SIEM) and security automated response (SOAR) solution that provides security analytics and threat intelligence across an enterprise
- A playbook is a collection of procedures that can be run from Azure Sentinel in response to an alert
- A security playbook can help automate and orchestrate your response, and can be run manually or set to run automatically when alerts are triggered
- Playbooks can be used to sync you Microsoft Sentinel incidents with other ticketing system
- Connector and Integrations:
- Ofiice 365
- Azure Active Directory
- Azure Advances Threat Protection
Azure Key Vault
Stores application secrets in a centralized cloud location to securely control access permission and access logging
- Securely store cryptographic keys and other secrets
- Secret management
- Key management
- Certificate management
- Storing secrets backed by hardware security modules (HSMs)
Azure Dedicated Host
Provides physical servers that host one or more Azure virtual machines that is dedicated to a single organizations workload
- Hardware isolation at the server level
- Control over maintenance event timing
- Aligned with Azure Hybrid Use Benefits
Network Security
Defense in depth
- Layered approach to securing computer system
- Provides multiple levels of protection
- Attacks against one layer are isolated from subsequent layers
- Combining network security solutions to maximize the defense
Network Security Groups (NSG)
Filter network traffic to and from Azure resources on Azure Virtual Networks
- Set inbound and outbound rules to filter by source and destination IP address, port, and protocol
- Add multiple rules, as needed, within subscription limits
- Azure applies
Application Security Groups (ASG)
- Enable you to group servers based on applications running on them and manage security for them as a group
- Rather than apply rules in the NSG to the VMs where applicaction servers reside, you create a ASG and add VMs to it, and then create the NSG and reference the ASG in it
- The NSG rules then apply to the VMs in the ASG
Azure Firewall
A stateful, managed Firewall as a Service (FaaS) that grants/denies server access based on IP address, in order to protect network resources in the perimeter layer
- Applies inbound and outbound traffic filtering rules
- Built-in high availability
- Unrestricted cloud scalability
- Uses Azure Monitor logging
Azure Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection
DDoS attacks overwhelm and exhaust network resources, making apps slow or unresponsive
- Sanitizes unwanted network traffic before it impacts service availability
- Basic service tier is automatically enabled in azure
- Standard service tier adds mitigation capabilities that are tuned to protect Azure Virtual Network resources
Identity, Governance, Privacy and Compliance
Azure Identity
Compare Authentication and Authorization
Authentication:
- Identifies the person or service seeking access to a resource
- Requests legitimate access credentials
- Basis for creating secure identity and access control principles
- Can use certificates to identify a person or service
Authorization:
- Determine an authenticated person or service level of access
- Defines which data they can access, and what they can do with it
- Can not use passwords to identify a person
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication
Provides additional security for your identities by requering two or more elements for full authentication
- Something you know (password, pin)
- Something you possess (phone, key)
- Something you are (biometric control)
Azure Active Directory (AAD)
Is Cloud bases identity and access management service
- Authentication (employees sign-in to access resources)
- Single sing-on (SSO)
- Application management
- Business to Business (B2B)
- Business to Customer (B2C) identity services
- Device managements
- Plans:
- Azure AD Free: Provides management of users and groups, synchronization with on-premises AD, basic reporting, SSO, Microsoft 365
- Azure AD Premium P1: Includes all features in free along with the capability to access on-premise resources, support dynamic groups, self-service group management, Microsoft Identity Manager
- Azure AD Premium P2: All the P1 features along with Azure AD Identity protection for conditional access to apps and critical data, and Privileged Identity Management for discover, monitor, restrict access to resources
- Can integrate with RBAC to control who has access to specific Azure Resources, what actions they can take and what areas they can access
- To use RBAC in azure, you create a role assignment that consists of a security principal, role definition and scope
- Security Principal=who, Role=what, and Scope=where
Conditional Access
Is used by Azure Active Directory to bring signals together, to make decisions and enforce organizational policies
- User or Group Memberships
- IP Location
- Device
- Application
- Risk Detection
Azure Governance
Explore Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Fine-grained access management
- Segregate duties within the team and grant only the amount of access to users that they need to perform their jobs
- Enables access to the Azure portal and controlling access to resources
Resource Locks
- Protect your Azure resources from accidental deletion or modification
- Locks can not be applied to specific users or roles, it applies to all users and roles
- Manage locks at subscription, resource group, or individual resource levels within Azure Portal
- Two Types:
- CanNotDelete ( You can read, update but not delete)
- ReadOnly ( You can read, but not update or delete)
Tags
- Provides metadata for your Azure resources
- Useful to differentiate areas in your company
- Up to 50 tag per resource by default
Azure Policy
Helps to enforce organizational standards and to access compliance at-scale. Provides governance and resource consistency with regulatory compliance, security, cost, and management
- Evaluates and identifies Azure resources that do not comply with your policies
- Provides built-in policy and initiative definitions, under categories such as Storage, Networking, Compute, Security Center, and Monitoring
Azure Policy Initiative
- Is a collection of Azure policies definitions, usually grouped with the aim of achieving a single goal
- Initiatives are used to simplify managing and assigning policies
- When a initiative assignment is evaluated, all policies in that initiative are evaluated
- An initiative can only contain policies that area located in the same subscription, however you can assign a single initiative to scopes across multiple subscriptions or management groups
Azure Blueprints
Makes it possible for development teams to rapidly build and stand up new environments. Developments team can quickly build trust through organizational compliance with a set of built-in components (such as networking) in order to speed up development and delivery
- When a blueprint is updated and the updated version is published, any assignments of the blueprint are not updated automatically
- When a blueprint is unassigned, all resources assigned by the blueprint remain in place, but blueprint resource locking is removed, this results int the deletion of the blueprint assignment object
- When you delete a core blueprint, any assigned versions of the blueprint remain in place, a blueprint must be unassigned before it can be deleted
- Role Assignments
- Policy Assignments
- Azure Resource Manager Templates
- Resource Groups
Cloud Adoption Framework
- The one Microsoft approach to cloud adoption in Azure
- Best practices from Microsoft employees, partners and customers
- Tools, guidance, and narratives for strategies and outcomes
- Strategy: Define the business justification and the expected outcomes of adoption
- Plan: Align actionable adoption plans with business outcomes
- Ready: Prepare the cloud environment for the planned changes
- Develop new cloud-native or hybrid solutions
Azure Compliance
Security, Privacy and Compliance
- Security: Secure by design. With built in intelligent security, Microsoft helps to protect against known and unknown cyberthreats, using automation and artificial intelligence
- Privacy: We are committed to ensuring the privacy of organizations through our contractual agreements, and by providing user control and transparency
- Compliance: We respect local laws and regulations and provide comprehensive coverage of compliance offerings
Online Service Terms and Data Protection Addendum
- Online Service Terms: The licensing terms define the terms and conditions for the products and Online Services you purchase through Microsoft Volume Licensing programs
- Data Protection Addendum: The DPA sets forth the obligations, with respect to the processing and security of Customer Data and Personal Data, in connection with the Online Services
Azure Pricing and SLA
Planning and managing costs
Factors affecting costs
There are six primary factors affecting costs
- Resource type
- Services: Azure usage rates and billings can differ between Enterprise, Web Direct, and CSP customers
- Location
- Bandwidth: inbound data is free, but outbound is priced based on zones
- Reserved Instances: reservations reduce your resource costs up to 72% on pay-as-you-go prices
- Azure Hybrid Use Benefit: For customers with Software Assurance, you can use your licenses on Azure to reduce costs
Pricing Calculator
- You can estimate the total costs of the services your are willing to use
- You only need to select the resource and specify the parameters like region, OS, tier, time
- You can export, save or share the price for the solution
Total Cost Ownership Calculator (TCO)
- A tool to estimate cost saving you can realize by migrating to Azure
- A report compares the costs of on-premises infrastructures with the costs of on-premises infrastructures with the costs of using Azure products and services in the cloud
Azure Cost Managements
- Reporting billing reports
- Data enrichment
- Budgets - set spend budget
- Alerting - when costs exceed limits
- Recommendation - cost recommendations
Azure SLAs and Service Lifecycle
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) describes Microsoft commitments for uptime and connectivity
- SLAs are based on individual products and services
SLAs for Azure products and services
- Performance targets are expressed as uptime and connectivity guarantees
- Performance-targets range from 99% to 99.999%
- If a service fails to meet the guarantees, a percentage of the monthly bill can be refounded
Composite SLAs
- Is the result of combining services with potentially differing SLAs, for example VMs and Azure SQL Database, one with 99.9 percent and the other with 99.99 percent, to determine the composite SLA, you simply multiply the SLA values for each resource
Actions that affect SLAs
Lower you SLA:
- Adding more services
- Choosing free or non-SLA services
Raise your SLA:
- Availability Zones
- Redundant systems Many factors can raise or lower your SLA, design decisions based on business goals will drive your SLA goals
Service Lifecycles
Determines how a product is released and supported, azure provides two lifecycle phases: preview and general availability
Azure Preview Program
- Azure features in the preview phase (beta testing)
- Preview features are not subject to SLAs and the limited warranty outlined in the Online service terms
- In general public previews are available to everyone, in some cases Microsoft offer private previews to selected organizations by invitation
- Can be configured at the organization or user level
General Availability
- The next step is general availability, these services are subject to the published SLAs and other service terms and warranties defined by the Online Service Terms
- Moving the GA does not guarantee that a service will always be offered
- Azure provides for a minimum of 12 months notice before a GA feature is retired